Figure 4.
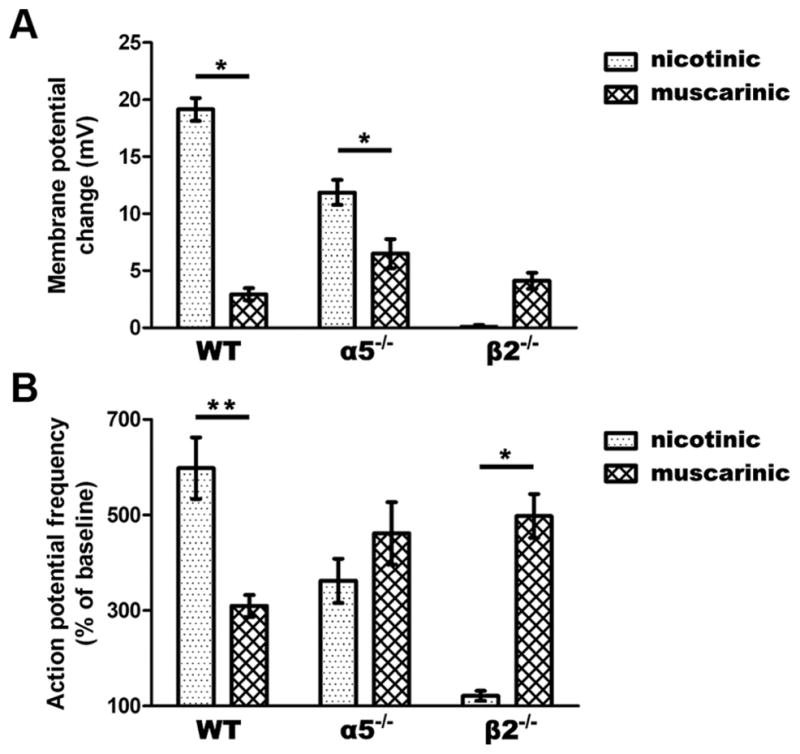
The balance of nicotinic to muscarinic excitation is shifted in α5 −/− and β2 −/− compared to WT neurons. A, There is a significant interaction in the degree of nicotinic and muscarinic depolarization across genotypes (p < 0.0001). Nicotinic stimulation contributes more to membrane depolarization in WT and α5 −/− neurons (*p <0.01). B, A significant interaction is found in the increase in action potential firing by nicotinic versus muscarinic stimulation across genotypes (p <0.0001). Nicotinic stimulation increases spiking frequency to a greater degree in WT neurons, while muscarinic stimulation makes a larger contribution in β2 −/− neurons (*p <0.01, **P <0.001).
