Figure 2.
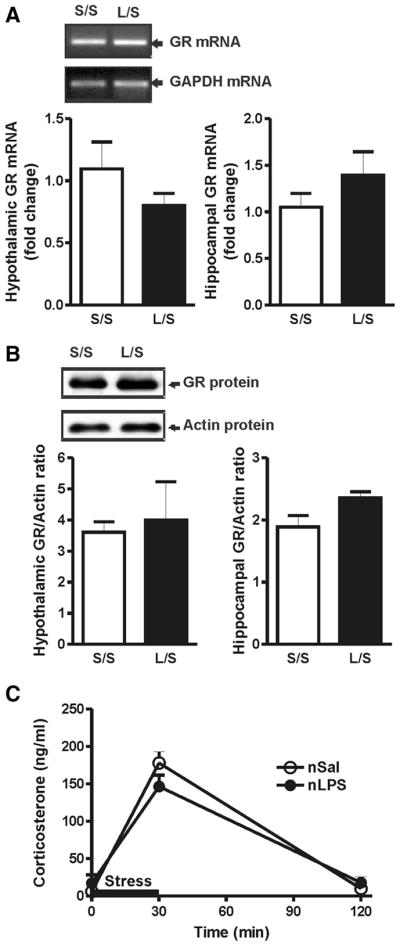
A, Sample gel of the amplified GR and GAPDH transcripts following real-time RT-PCR analysis and relative fold increase of GR mRNA in the hypothalamus and hippocampus. The levels of GR mRNA in animals treated with postnatal LPS or saline are not significantly different under basal conditions (L/S, n = 6 vs S/S, n = 6) in either the hypothalamus or the hippocampus. B, Sample Western blot of GR and actin protein levels and the ratio of GR/actin in the hypothalamus and hippocampus. The protein GR levels of postnatal LPS- or saline-treated animals are not significantly different under basal conditions (L/S, n = 4 vs S/S, n = 4) in either the hypothalamus or the hippocampus. C, Plasma corticosterone levels before, during, and after restraint stress applied for 30 min, as indicated by the black bar (S/S, n = 6 vs L/L, n = 6). S/S, postnatal saline + adult saline; L/S, postnatal LPS + adult saline; nSal, neonatal saline; nLPS, neonatal LPS. Data are mean ± SEM.
