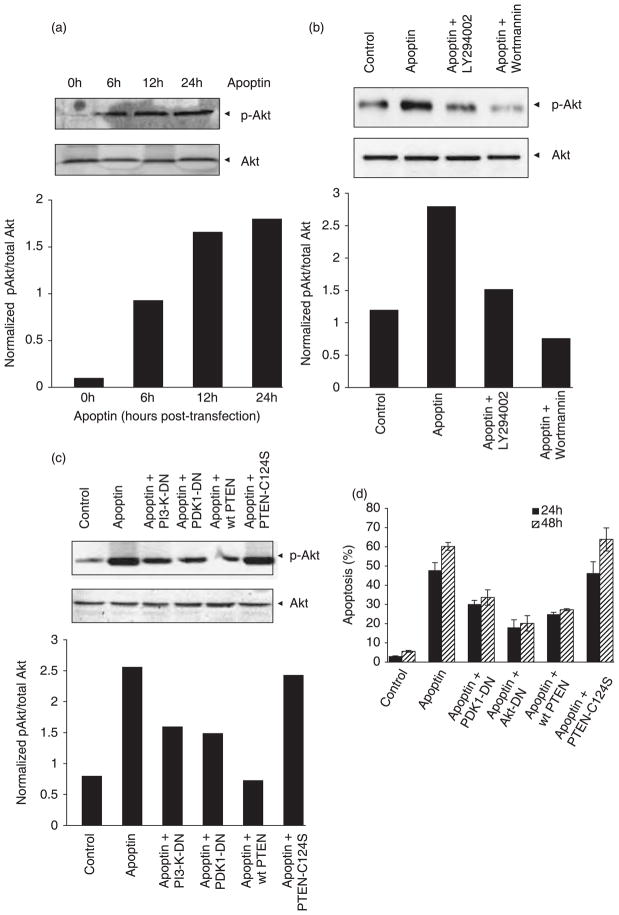
Figure 3. Akt is activated downstream of PI3-K during apoptin-induced cell death.
(a) The activation of Akt by apoptin was detected in PC-3 cells by immunoblotting, using an antibody against Akt-phosphorylated at Ser-473 (p-Akt) at different time points after transfection to express apoptin. Total Akt was detected by immunoblotting. Signals for total and phosphorylated Akt were then scanned and evaluated using ImageQuant 5.2 software. Normalized level of phosphorylated Akt is shown in the graph below. (b) PC-3 cells were transfected to express apoptin in the absence or presence of treatment with wortmannin or LY294002, and phosphorylated Akt, was then detected by immunoblotting. The normalized amount of phosphorylated Akt is shown in the graph below. (c) Akt activation was also determined by immunoblotting in lysates from cells transfected to express apoptin alone or apoptin together with either dominant-negative (DN) PI3-K, PDK1-DN, wild-type PTEN, or phosphatase-deficient C124S-PTEN mutant. The normalized amount of phosphorylated Akt is shown in the graph below. The significance of the data was statistically confirmed (P < 0.02) using Student’s t-test. (d) The effect of Akt inhibition on apoptin toxicity was assessed in PC-3 cells by flow cytometry (Nicoletti method), either 24 h or 48 h after transfection, to express apoptin either alone or together with PDK1-DN, Akt-DN (adenoviral vector), wild-type PTEN or C124S-PTEN. The results obtained were confirmed using the MTT assay (data not shown).