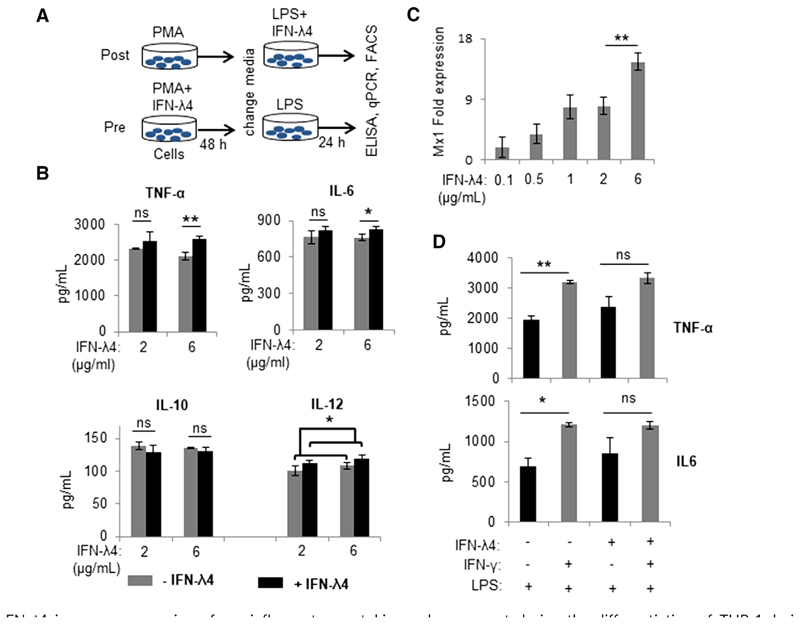
Figure 2.
IFN-λ4 increases expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines when present during the differentiation of THP-1-derived M1 macrophage-like cells. (A) Schematic representation of the two strategies (postand pretreatment) used to examine the effect of IFN-λ4 on macrophage-like cells. (B) IFN-λ4 significantly increased the secretion of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-12 in the pretreatment strategy (at a higher dose) showing the mean and SD. (C) MX dynamin-like GTPase 1 (Mx1) expression in A549 cells treated for 24 h with graded doses of IFN-λ4. The data from THP-1-derived macrophage-like cells activated toward an M1 phenotype by LPS treatment. The data are from three biological replicates show the mean of technical replicates with error bars showing the SD (a significant difference, P < 0.01, in the expression of Mx1 between 2 and 6 μg/ml of recombinant IFN-λ4 was observed). (D) IFN-λ4 and IFN-λ may activate overlapping pathways. THP-1-derived macrophage-like cells differentiated with ±IFN-λ4 were activated to an M1 phenotype by using LPS and ±IFN-λ. The data are from three biological replicates showing the mean and SD. For (B), (C), and (D) *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ns, not significant