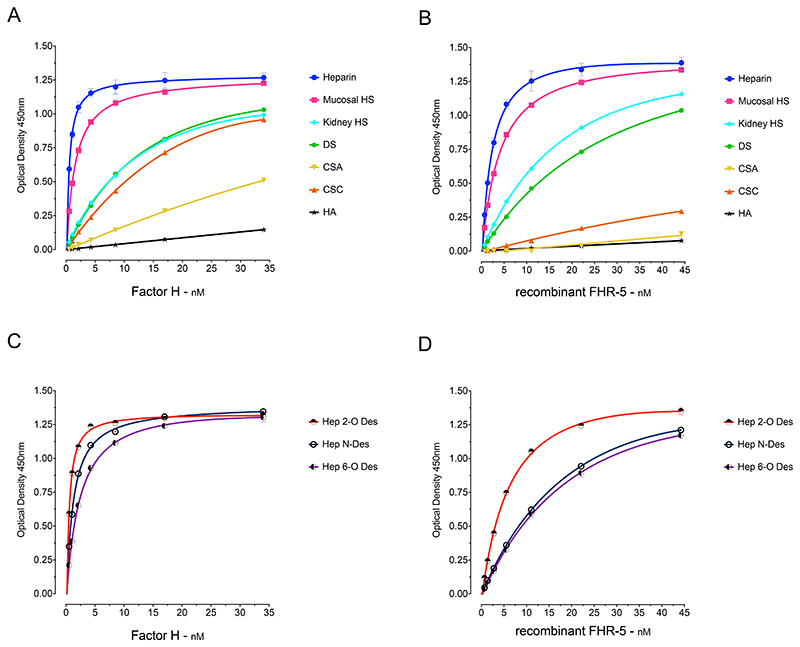
Figure 1. Binding of Factor H (FH) and recombinant Factor H FHR-5 (rFHR-5) to surface-immobilised GAGs.
(A) FH and (B) rFHR-5 showed dose-dependent binding correlating with the degree of GAG sulfation and lack of binding to the non-sulfated GAG, hyaluronic acid. (C) FH and (D) rFHR-5 binding to surface-immobilized, selectively desulfated GAGs showing reduction of binding after desulfation. The data are representative of more than ten independently performed experiments using the GAGs and representative of two independently performed experiments using the selectively de-sulphated GAGs. Data points represent mean of two replicates with standard deviation. HS, heparan sulfate; DS, dermatan sulfate; CSA, chondroitin sulfate A; CSC, chondroitin sulfate C; HA, hyaluronic acid. Hep 2-O-deS, heparin desulfated at the 2-O position of the iduronic acid; Hep 6-O-deS, heparin desulfated at the 6-O position of the iduronic acid; Hep N-deS-reAc, heparin desulfated at the N-position of the glucosamine followed by N-reacetylation.