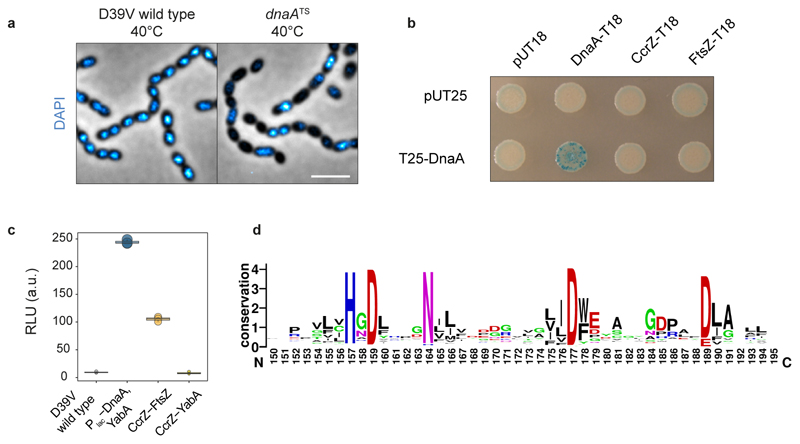
Extended Data Fig. 4. CcrZ activity is crucial for proper replication initiation as a dnaATS mutant phenocopied a ccrZ deletion.
a, Microscopy of DAPI-stained DnaA thermosensitive strain at non-permissive temperature (40°C) indicates several anucleate cells, compared to a wild type grown in identical conditions. Scale bar, 3 μm. b, No interaction was detected between DnaA and CcrZ using bacterial-2-hybrid, while a positive DnaA-DnaA self-interaction is visible. c, Using split-luc assay, no interaction between CcrZ-YabA was detected, while a strong signal was obtained for DnaA-YabA. DnaA level was controlled by Plac to avoid toxicity. Each circle represents the average of n=15 measurements of a technical replicate, with the size of the dot representing the SEM. d, Five (H157, D159, N164, D177 and D189) most conserved residues between 1000 different CcrZ sequences from different bacterial species; sequences obtained from UniRef50 database.