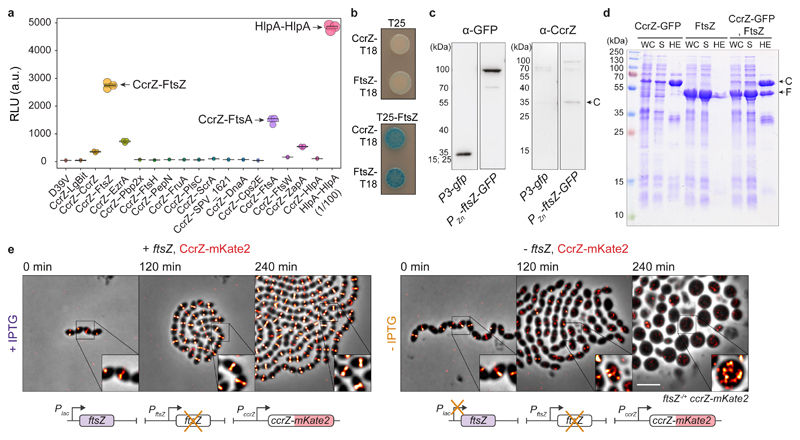
Fig. 3. CcrZ directly interacts with FtsZ.
a, Split-luciferase assay using several combinations with CcrZ-LgBit reveals that CcrZ and FtsZ are in very close proximity, as indicated by a high luminescence signal. FtsA, EzrA and ZapA, all three interacting directly with FtsZ, also gave a slight signal. hlpA-LgBit hlpA-SmBit (HlpA-HlpA), here diluted 100 times, is used as positive control. Each dot represents the average of n=15 measurements of a technical replicate, with the size of the dot representing the SEM. b, FtsZ-CcrZ interaction confirmation by bacterial two-hybrid assay. T25 is the empty vector pST25 and T25-FtsZ corresponds to vector pST25-FtsZ used in combination with pUT18-CcrZ (CcrZ-T18) and pUT18-FtsZ (FtsZ-T18). c, Affinity purification of FtsZ-GFP from S. pneumoniae cells (2nd lane) also pulls down untagged CcrZ (4th lane). Purification of GFP alone (first lane) did not pull CcrZ down (3rd lane). d, FtsZ from S. pneumoniae expressed in E. coli co-purifies with CcrZSp-GFP by affinity purification. WC: whole cell extract, S: supernatant, HE: heat eluted products, C: CcrZ-GFP, F: FtsZ. e, Epifluorescence time-lapse microscopy of CcrZ-mKate2 at 37°C in presence (left panel) or absence (right panel) of FtsZ. When FtsZ amounts are reduced, cells increase their size and CcrZ is de-localized from mid-cell. Scale bar, 3 μm.