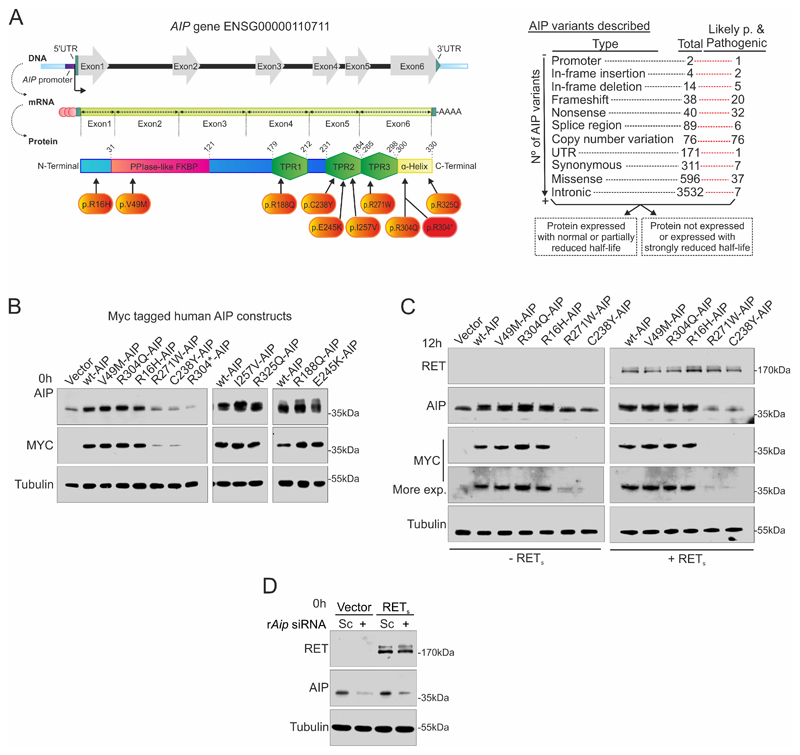
Figure 1. Strategy to study the two groups of AIP variants: shorter and normal half-life.
A) Left: Cartoon showing the human AIP gene, mRNA and protein. The studied variants are indicated. Right: AIP gene variants described in Ensembl (data retrieved at 06/20/2020), indicating how many of each type of variants is considered as pathogenic, likely-pathogenic (Likely p.) as opposed to Variants of Uncertain Significance, likely non-benign or benign. Variants could be grouped based on their protein half-life. B) Wild-type human AIP (wtAIP) or variant AIP were expressed in the pituitary somatotroph rat cell line GH4C1 with an N-terminal MYC-tag. Western blot against AIP detected endogenous rat AIP together with exogenous human AIP. MYC western blot exclusively detected transfected human AIP. R304* AIP is undetectable under our experimental conditions presenting a very-short half-life, R271W and C238Y present short half-life in comparison to wtAIP, while R16H, V49M, R188Q, E245K, I257V, R304Q and R325Q AIP variants present normal half-life compared to wtAIP. C) Co-transfection of RET receptor does not alter the half-life distribution of wtAIP or AIP variants. D) Aip siRNA is able to downregulate endogenous rat AIP protein expression as a model for AIP deficiency in GH4C1 cells.