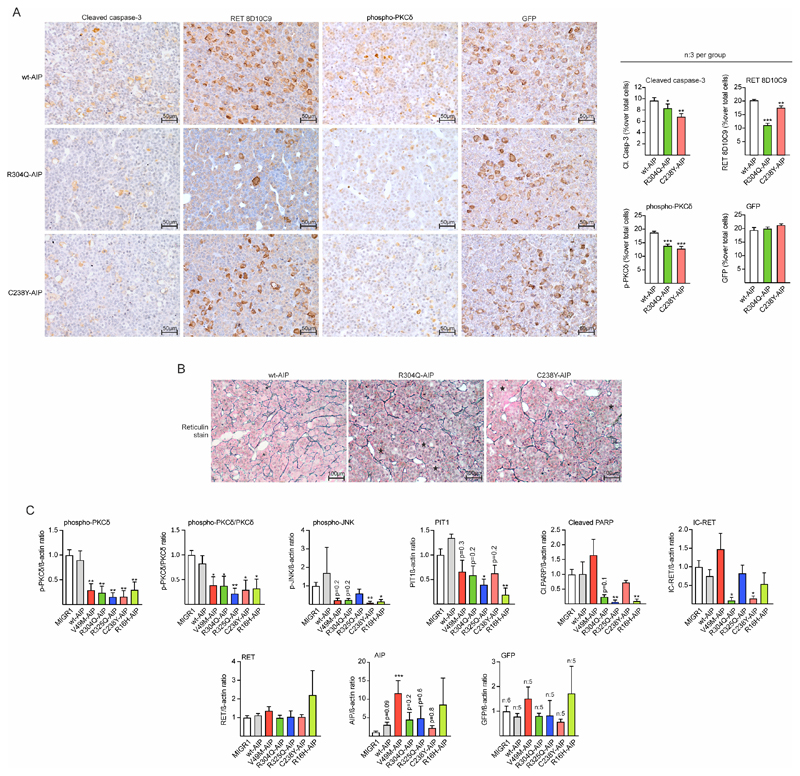
Figure 6. AIP pathogenic mutations injected in the pituitary at birth block the RET/caspase-3/PKCδ/PIT1 apoptosis pathway in male rats inducing hyperplasia.
A) Left: Microphotographs of immunohistochemistry for cleaved caspase-3, IC-RET (monoclonal RET8D10C9 antibody), p-PKCδ, and GFP (for EGFP detection) in sections of wt or variant AIP injected pituitaries. Sections from three independent animals per group were mounted in the same slide (20x magnification, bar=50 μm). Right: Immunohistochemistry was quantified compared to total nuclei. While there were no significant differences in the % of GFP cells, the % of cleaved caspase-3, IC-RET and p-PKCδ stained cells was significantly reduced in variant AIP pituitaries respect to wtAIP pituitaries. B) Reticulin staining in the same pituitaries as in A. Partial disruption of the reticulin network with extended acini is observed (asterisks) in the variant AIP pituitaries. C) Protein quantification respect to controls (loading control: beta-actin) of the western blot performed in groups (n=4) of pituitary extracts from vector (MIGR1), wtAIP or variant AIP. High throughput gels for 22 samples were used to run extracts in parallel. Significant reductions in p-PKCδ and p-JNK were found. Cleaved PARP was also reduced in variant AIP pituitaries except for V49M. PIT1 and IC-RET were significantly reduced in some variants but in other results did not reach significance. Levels of RET, AIP and exogenous GFP were non-significant between groups.
(Kruskall-Wallis with Dunn’s multiple comparison test correction, A; One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test correction C. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; numbers, when p is non-significant but is small)