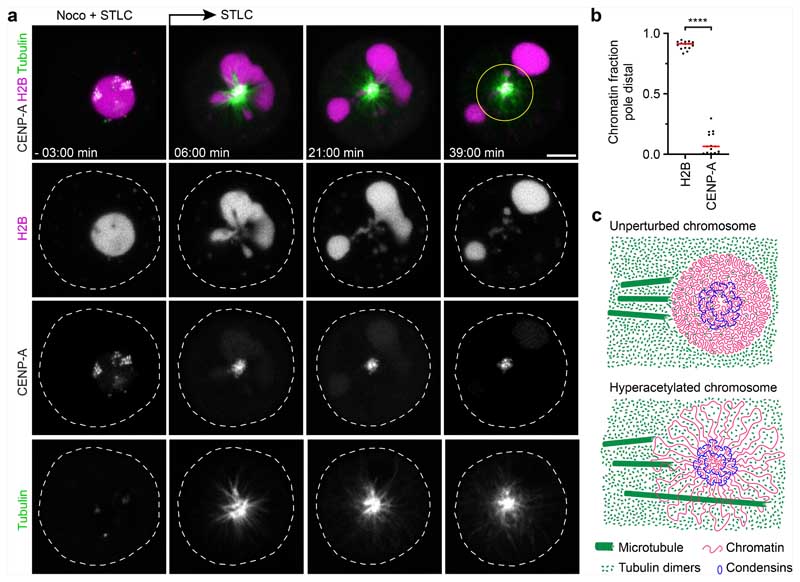
Fig. 4. Microtubules push liquified chromatin away from the spindle pole.
a, Time-lapse microscopy analysis of liquified chromatin during monopolar spindle assembly. AluI was injected into live mitotic HeLa cells expressing H2B–mCherry and meGFP-CENP-A, stained with SiR–tubulin, in the presence of nocodazole (noco) and STLC. Nocodazole was then removed at t = 0 min during time-lapse imaging to induce monopolar spindle assembly. Projection of 5 z-sections. Time is shown as min:s. b, Quantification of bulk chromatin (H2B–mCherry) and centromeric chromatin (meGFP-CENP-A) localizing at the cell periphery relative to the region around the spindle monopole at t = 36 min. n = 15 cells. The bars indicate the mean. Significance was tested by a two-tailed Mann-Whitney U-test (P = 1.289 × 10−8). c, Model of chromatin compaction and condensin-mediated DNA looping in mitotic chromosome and spindle assembly. The illustration shows a top-down view of a chromosome cross-section. Biological replicates: n = 3 (a,b). Scale bars, 5 μm.