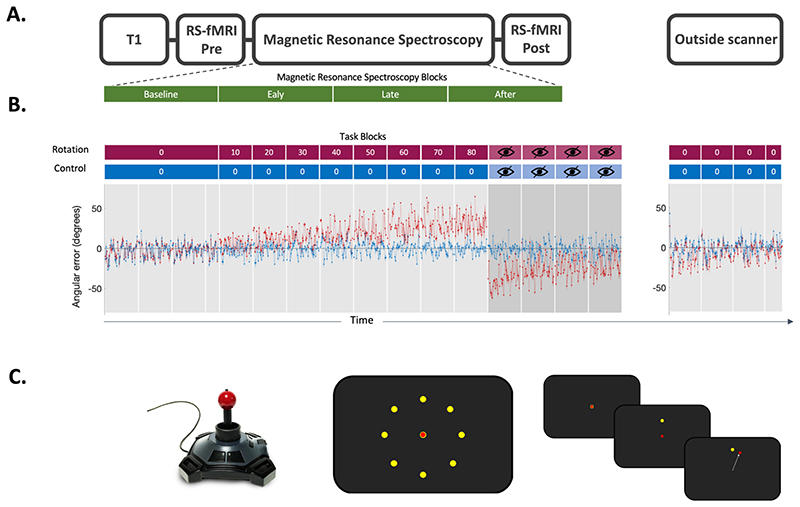
Fig. 1. Experiment.
A. Scanning Protocol.
T1-weighted structural image was acquired at the begin of the MRI scan. Resting-state fMRI data was acquired before and after the task. Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Imaging (MRSI) data was acquired during the task. Four MRSI scans were acquired during performance of the visuomotor task with each MRSI scan lasting 9 min, total acquisition 36 min.
B. Behavioural data.
Participants used a joystick to shoot targets on a screen. Participants began by performing 136 trials with no rotation imposed serving as the baseline in both conditions. In the rotation condition (red blocks), stepwise increasing rotated visual feedback required participants to adapt movements to reduce errors. One block at each angle and each block consisted of 40 trials of 4 seconds duration each. The numbers in the red and blue boxes indicate the degree to which the visual feedback was rotated, with 0° indicating no rotation. The imposed rotation reached a maximum of 80°, after which visual feedback was removed for four blocks of 40 trials each (blocks with crossed out eye). In the control session (blue blocks), participants performed the task without any rotation imposed, but for the same length (480 trials in total for the main task). The rotation was washed out after task (144 trials, no rotation). The task was practised before the main task outside of the scanner (32 trials, no rotation; not depicted in this figure). Behavioural data is shown as angular error at each trial averaged across participants. Shaded area represents standard error of the mean. Rotation condition error is shown in red. Control condition error is shown in blue. Target sequence was fixed across participants and across sessions.
C. Task Schematic.
Left. MR-compatible Joystick used to record participant responses.
Middle. Eight possible target locations (yellow) centred radially around the cursor (red) at its starting position. Right. Schematic of a rotation trial. Cursor (red) is first presented at the centre starting position. Target (yellow) appears at one of the eight possible target locations. Participant makes a centre-out movement towards the target, but sees clockwise rotated visual feedback.