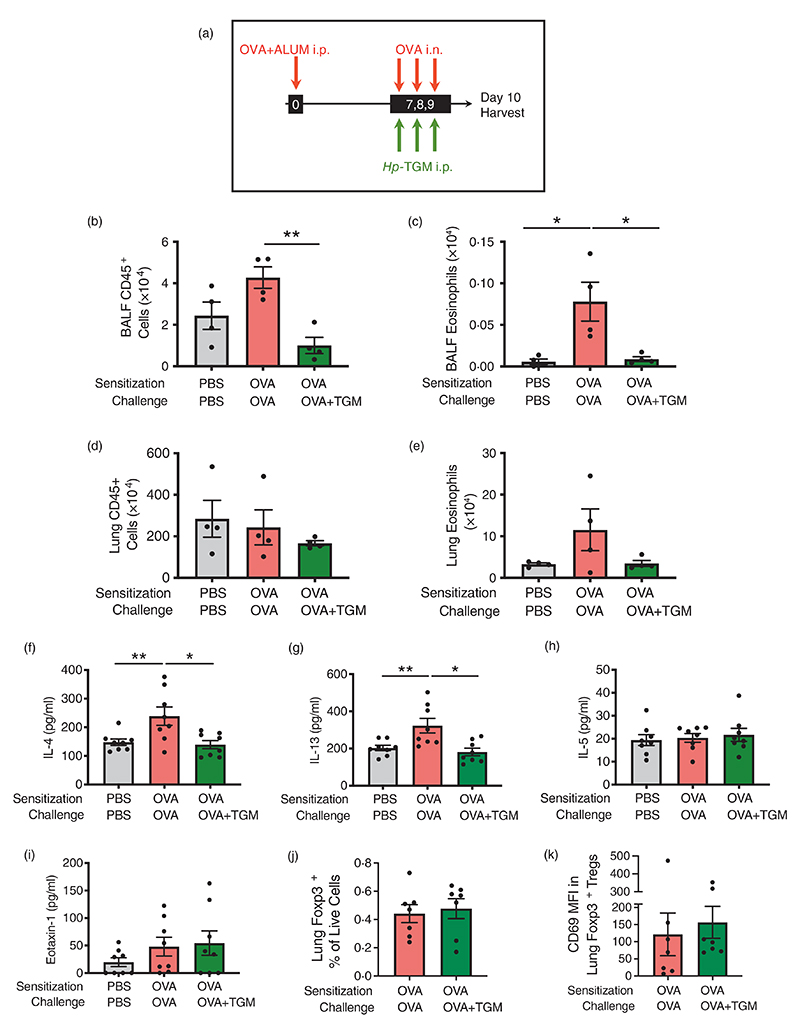
Figure 6.
Hp-TGM blocks allergic eosinophilia during an OVA challenge. Mice were sensitized with Ovalbumin (OVA, 20 μg) intraperitoneally at day 0. OVA was then intranasally administered daily from day 7 to day 9 (20 μg) and Hp-TGM (1 μg) was administered intraperitoneally every day of challenge. Mice were then culled at day 10. (a) Schematic representation of the experimental protocol. (b–e) CD45+ cell and eosinophil cell numbers were enumerated in BALF (b and c) and lung (d and e). (f–i) Type 2 cytokines were measured in lung homogenates, showing IL-4, IL-13, IL-5 and eotaxin-1. (j) Frequency of Foxp3+ Tregs in lung homogenates of mice sensitized and challenged with OVA, in the absence or presence of Hp-TGM administration. (k) Expression of CD69 within the Foxp3+ Treg population in lung homogenates of mice sensitized and challenged with OVA, in the absence or presence of Hp-TGM administration. Data are from ≥2 independent experiments. Data shown are pooled from two experiments (n = 7–9). All data were analysed using Prism (Graphpad Software Inc.), one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons post-test was used to compare multiple independent groups. Mean values and SEM are indicated. **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05; non-significant differences not shown.