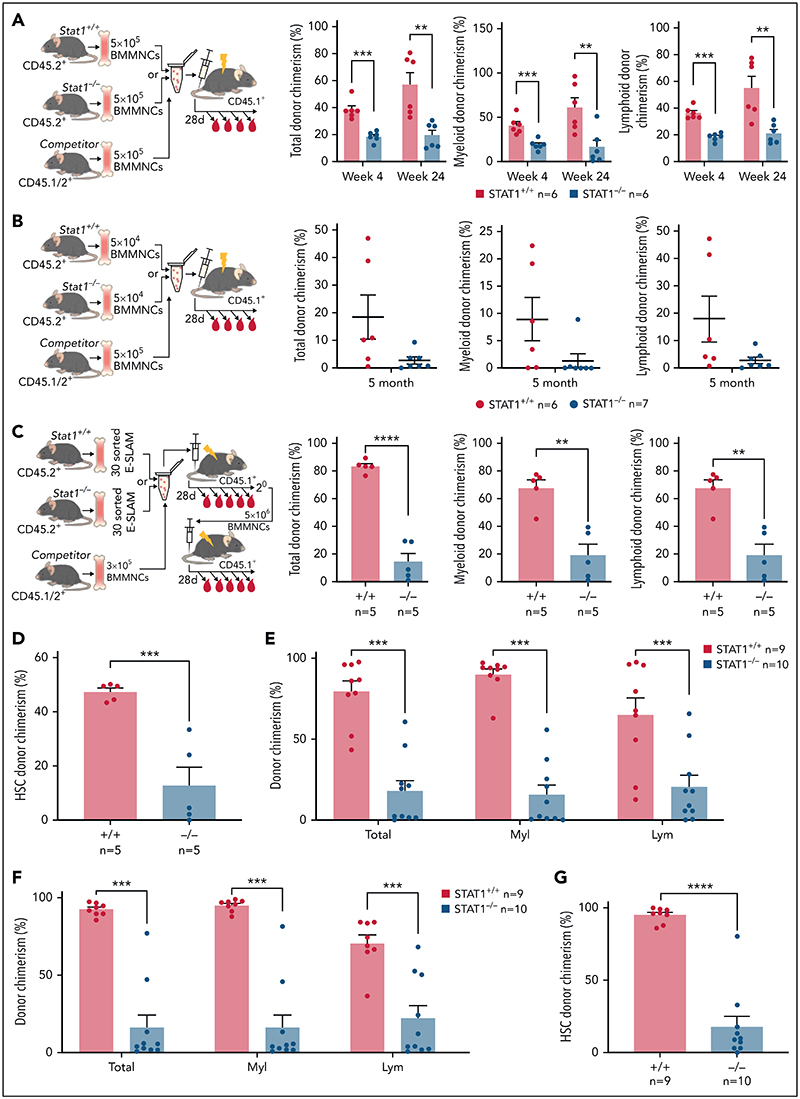
Figure 2. HSCs from STAT1KO mice show functional defects in competitive transplants.
(A) STATI-deficient bone marrow (BM) cells exhibited reduced repopulating capacity in competitive transplant recipients. 5 × 105 BM cells (CD45.2+) from STAT1KO or WT control mice were mixed with an equal number of competitor cells (CD45.1+/45.2+) and transplanted into lethally irradiated CD45.1 recipient mice. Donor repopulation was assessed using flow cytometry of nucleated peripheral blood with antibodies for CD45.1 and CD45.2 to distinguish donor origin: Ly6g and Mac1 for myeloid and B220 and CD3e for lymphoid cells. Bar graphs show the competitive repopulating ability of donor cells presented as the percentage of repopulated cells derived from test donor cells among the total number of donor-derived cells (y = test/[test + competitor]). (B) Bone marrow cells from STAT1KO mice contained a lower number of functional HSCs as shown by chimerism at 5 months posttransplantation. Competitive bone marrow transplantation was performed and analyzed as (A) using low-dose (5 × 104) BM cells from WT or STAT1KO mice. At 5 months posttransplantation, 6 out 7 recipients receiving STAT1KO BM cells were found to have donor chimerisms <0.5% in myeloid lineage (5 with 0% and 1 with 0.2%), whereas only 2 recipients receiving STAT1+/+ BM had chimerisms <0.5% (1 with 0% and 1 with 0.1%). (C) ESLAM HSCsfrom STAT1KO mice displayed reduced repopulation capacity. 30 ESLAM HSCs FACS isolated from STAT1KO or WT control mice and mixed with 3 × 105 CD45.1+/CD45.2+ competitor bone marrow cells were transplanted into lethally irradiated CD45.1 recipients. Repopulating capacity in bone marrow was analyzed as in (A). (D) Frequency of ESLAM HSCs derived from STAT1KO donor was reduced. At 6 months posttransplantation in (C), bone marrow cells from the recipient mice were assessed for donor-derived HSC chimerism using flow cytometry. ESLAM HSC was defined as CD45+CD150+CD48-EPCR+, and donor origin was distinguished using antibodies for CD45.1 and CD45.2. (E-F) ESLAM HSCs from STAT1KO mice displayed reduced repopulation capacity in blood (E) and bone marrow (F) in secondary transplant. 5 × 106BMcells from the primary recipients in (C) were transplanted into secondary recipients (CD45.1+), and donor repopulation was assessed as in (A). (G) Frequency of ESLAM HSCs derived from STAT1KO donor was reduced in secondary transplant recipients at 5 months posttransplantation. Data are shown as mean ± standard error; asterisks indicate significant differences by Student t test (*P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001; ****P < .0001).