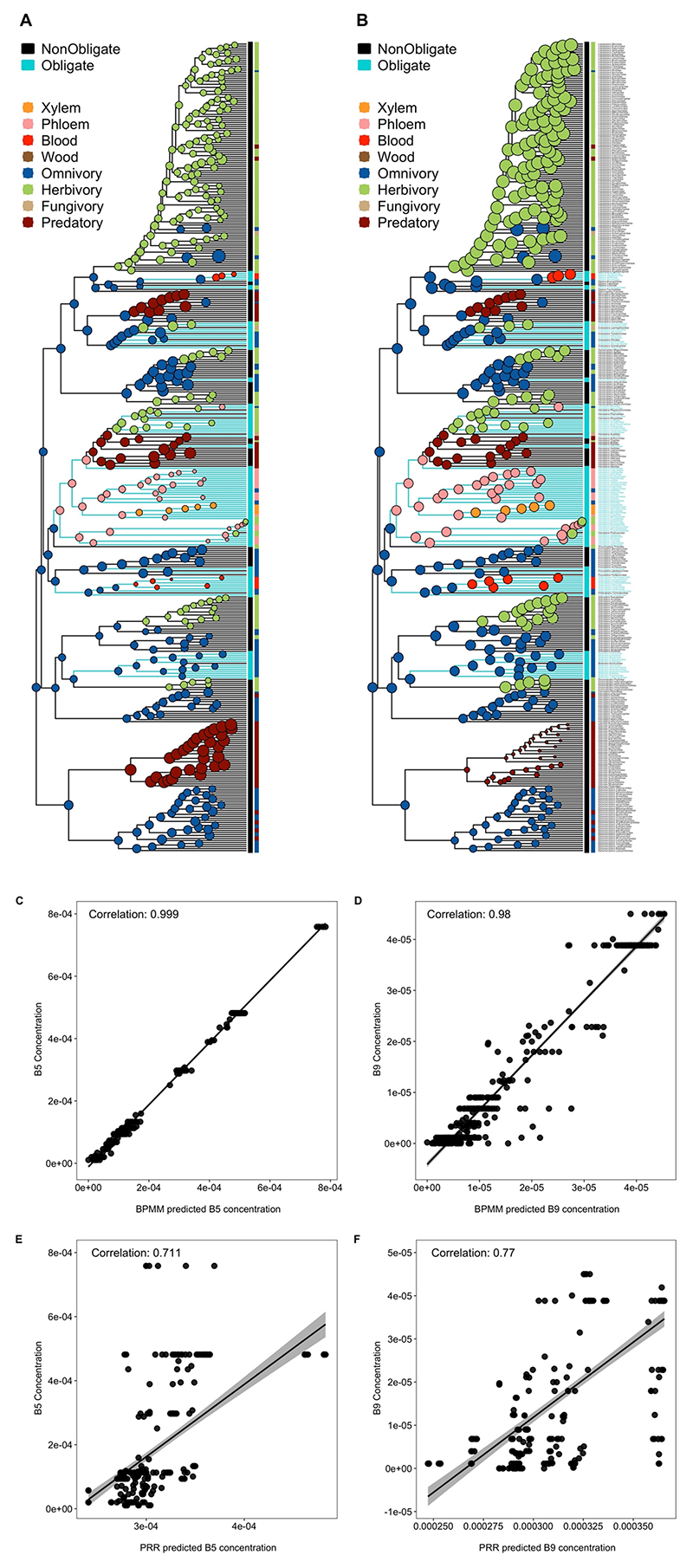
Extended Data Fig. 4. Reconstruction of ancestral levels of B vitamins, obligate symbiosis and feeding niches across 402 insect families.
Ancestral concentrations of (A) B5 and (B) B9 vitamins were estimated using BPMMs and are shown by the size of circles at each node. Turquoise tips and branches indicate obligate symbionts and different coloured dots represent different feeding niches. Ancestral feeding niches were estimated using SCM and states of obligate symbiosis were estimated using a BPMM (Supplementary Table 5). There was greater correspondence between predictions from BPMMs and raw concentrations of (C) B5 and (D) B9 vitamins than there was for predictions from phylogenetic ridge regressions (PRR, E-F), which allowed for rate shifts in B vitamins across the phylogeny (E-F). In C-F lines represent linear regressions with 95% confidence intervals (shaded bands).