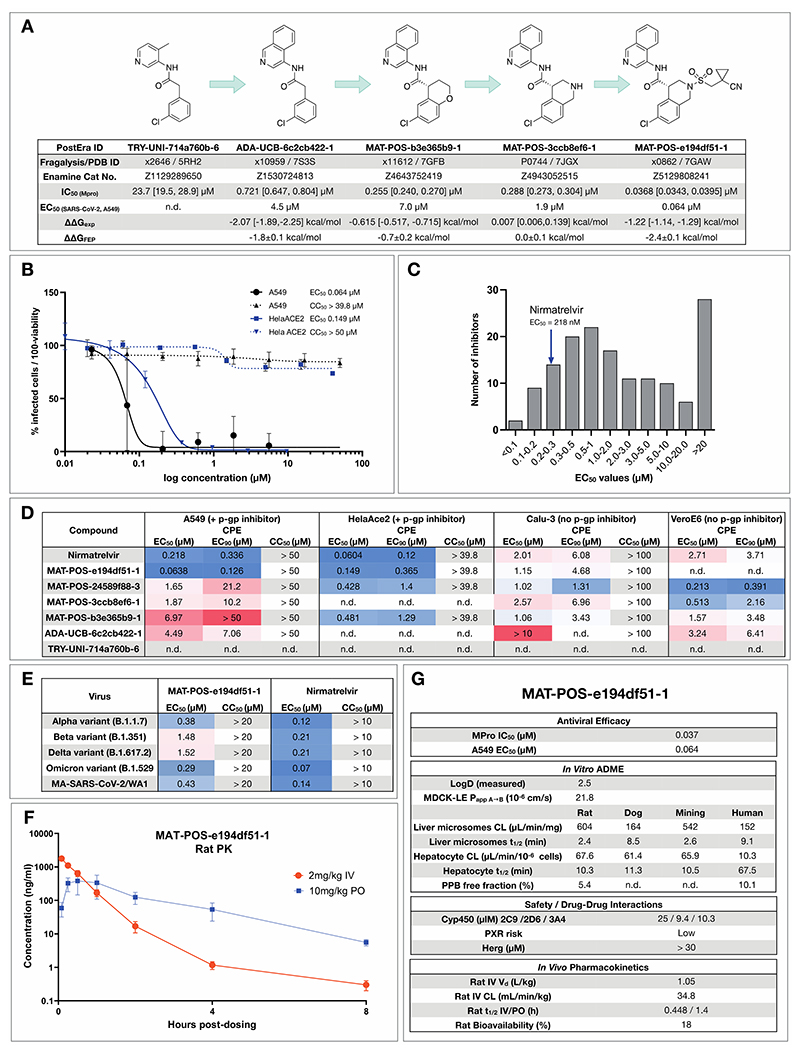
Figure 5. Iterative medicinal chemistry furnished an orally bioavailable inhibitor.
A: Summary of key medicinal chemistry milestones in developing the initial crowdsourced lead compound into a potent antiviral. X-ray structures for each milestone compound are available via Fragalysis, and each compound can be obtained from Enamine via the corresponding catalogue numbers. Retrospective alchemical free energy calculation predictions for each transformation (ΔΔGFEP) are shown for each step between milestones, along with the corresponding experimental free energy difference (ΔΔGexp) derived from biochemical activities. As positive control, under our assay condition Nirmatrelvir has IC50 of 2.6nM.
B: Antiviral activity of MAT-POS-e194df51-1 cellular antiviral assays, with an EC50 of 64 nM in A549-ACE2-TMPRSS2 cells assessing cytopathic effect (CPE, black, plotted as 100 - % viability), and 126 nM in HelaAce2 assays (blue, plotted as % infected cells). Both assays were performed with p-gp inhibitors.
C: Histogram comparing antiviral efficacy of all COVID Moonshot compounds measured to date in an A549-ACE2-TMPRSS2 CPE cellular antiviral assay.
D: Detailed cellular antiviral assessment of key compounds comprising the synthetic strategy (Fig 5A) across different cell lines and assay techniques, with and without p-gp inhibitors, demonstrating efficacy of MAT-POS-e194df51-1 in various set-ups and laboratories.
E: MAT-POS-e194df51-1 shows good cross-reactivity against known circulating variants of SARS-CoV-2 in antiviral cellular assays in a CPE assay in HelaACE2 cells.
F: PK profile of MAT-POS-e194df51-1 in rats with a 2 mg/kg intravenous and 10 mg/kg oral dosing with good oral availability.
G: ADME characteristics of MAT-POS-e194df51-1 demonstrate a favorable safety profile, indicating translational potential of the lead series.