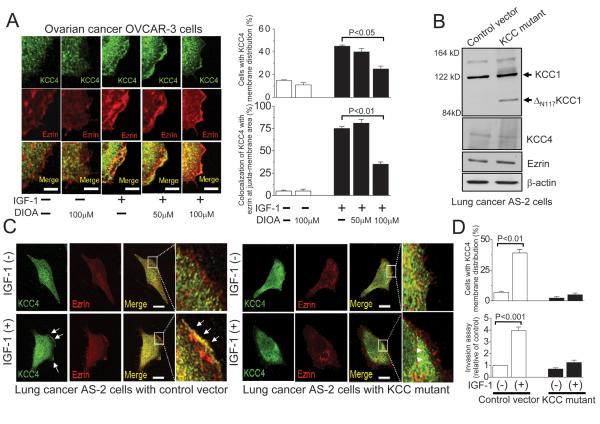
Figure 5. KCC activity is necessary for the membrane recruitment of KCC4 and ezrin.
(A) IGF-1 induced the extensive formation of lamellipodia, where KCC4 was associated with ezrin. DIOA, the KCC inhibitor, inhibited the colocalization of KCC4 and ezrin in a concentration-dependent manner. Ovarian cancer OVCAR-3 cells were pre-incubated with DIOA for 30 min, prior to 100 ng/ml IGF-1 stimulation. Each column for image analysis represents mean ± S.E.M. of at least 60 cells. Scale bar, 2 μm. (B) Overexpression of the loss-of-function KCC mutant (ΔN117KCC1) in lung cancer AS-2 cells. ΔN117KCC1: removal of the N-terminal 117 amino acids from KCC1. (C) The membrane recruitments of KCC4 and ezrin were almost abolished in loss-of-function KCC mutant cancer cells regardless of IGF-1 stimulation. Arrow: the association of KCC4 with ezrin at lamellipodia; Arrowhead: the cytosolic aggregation of KCC4. Scale bar, 5 μm. (D) The invasion assays and quantitative analyses of KCC4 recruitment were performed in different clones of lung cancer AS-2 cells. Each column in invasion assay represents mean ± S.E.M. from at least 5 different experiments. The invasive ability of cells with empty vector was used as the control. For image analysis, each column represents mean ± S.E.M. of at least 50 cells. Statistics were done by unpaired t test.