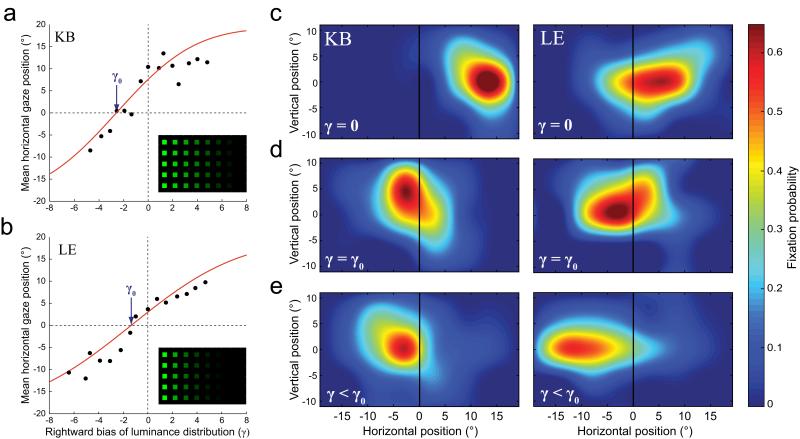
Figure 7. Counteracting the ipsilesional bias in neglect.
(a & b) Mean horizontal location of exploratory fixations on null trials as a function of bias of the background luminance (γ), for (a) patient KB and (b) patient LE. Red lines represent the cumulative gaussian functions that best fit each patient’s data; the arrows indicate the luminance bias (γ0) that minimizes the mean deviation of each patient’s exploratory fixations from the centre of the display. The corresponding search array is shown in the inset.
(c, d & e) Distribution of exploratory fixations on null trials for patient KB (left) and patient LE (right), when (c) display luminance is uniform (γ = 0), (d) luminance is adjusted to compensate for each patient’s rightward bias (γ = γ0), and (e) luminance is biased further to the left (γ < γ0).