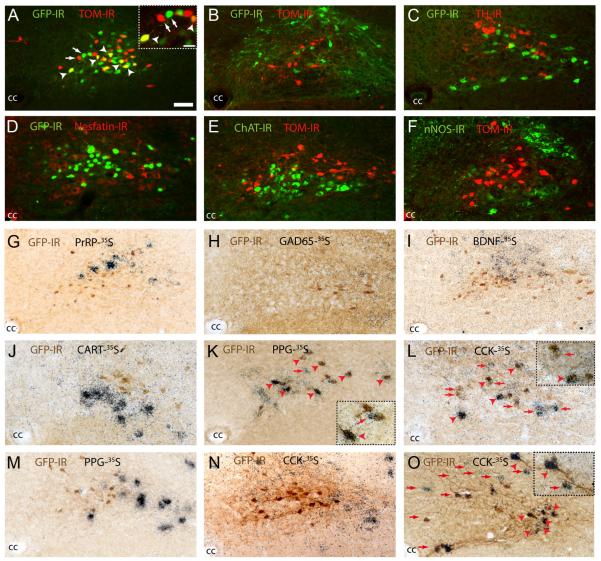
FIG. 2.
Neurochemical profiling of LepRb-expressing cells of the caudal NTS. A–F, Double-immunofluorescent analysis of LepRb-expressing neurons in compound LepRb-Ires-Cre::tdTOM/POMC-EGFP and LepRb-Ires-Cre::tdTOM/NPY-GFP mice revealed colocalization of LepRb-expressing neurons (red) with POMC-expressing (green; A) but not NPY-expressing (green; B) neurons of the NTS. Immunohistological analysis in LepRb-Cre::EYFP mice also demonstrated these cells to be negative for TH (C), nesfatin (D), ChAT (E), nNOS (F). G–L, Dual-immunohistological and in situ hybridization analysis demonstrated the absence of LepRb coexpression (brown cytoplasmic stain) with PrRP (G), GAD67 (H), BDNF (I), or CART (J) mRNA (black grains). However, LepRb neurons were found to express PPG/GLP1 (K) and CCK (L) mRNA. M–O, Population analysis of NTS LepRb-expressing neurons demonstrated that POMC-EGFP neurons did not express PPG/GLP1 (M) or CCK (N) but that a proportion of PPG/GLP1-YFP NTS neurons also exhibited CCK expression (O). Arrows represent single-labeled cells and arrowheads colocalized cells. cc, Central canal. Scale bar in A applies to A–I and represents 50 μm. Scale bar in A inset applies to insets in K, L, and O and represents 25 μm.