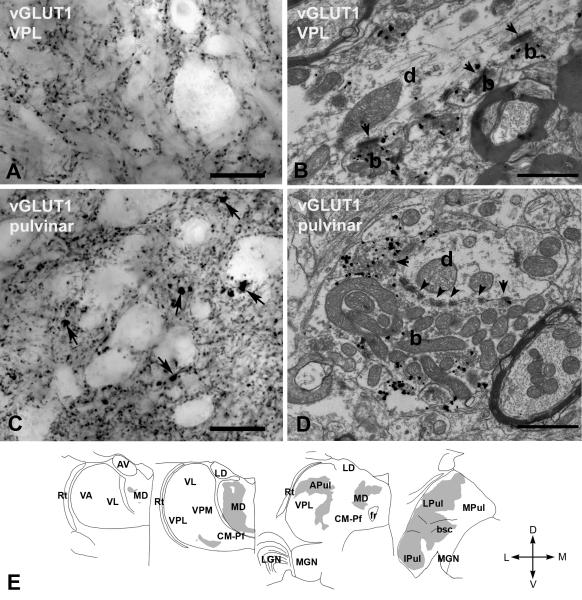
Figure 3. vGLUT1-immunoreactive terminals in the macaque thalamus.
A) High power light microscopic image of a vGLUT1-immunostained section from the ventral posterolateral nucleus (VPL) displaying small vGLUT1-immunoreactive terminals only.
B) At the electron microscopic level these terminals (b, silver intensified gold) display the features of RS-type terminals i.e. small size, maximum of one or two mitochodria, no puctum adherens and a single synapse (arrow). d, postsynaptic dendrite.
C) In the lateral pulvinar, besides the small vGLUT1-immunoreactive terminals, large immunoreactive structures (arrows) can also be distinguished at the light microscopic level.
D) At the electron microscopic level, a large vGLUT1-immunoreactive terminal (b, silver intensified gold) displays all the ultrastructural features of RL terminals. Arrows; synapses; arrowheads; puncta adherentia, d, postsynaptic dendrite.
E) Regional distribution of large vGLUT1-positive terminals at four coronal levels of the macaque thalamus. Note the lack of large vGLUT1-positve terminals from many thalamic nuclei considered as higher order and the heterogeneity of the distribution within the mediodorsal nucleus (MD) and pulvinar.
Scales: A and C, 20 μm; B and D 1 μm. Abbreviations: APul anterior pulvinar, AV anteroventral, bsc, brachium of superior colliculus, CM-Pf centromedian-parafascicular, fr fasciculus retroflexus, Ipul inferior pulvinar, LD laterodorsal, LGN lateral geniculate nucleus, LPul lateral pulvinar, MD mediodorsal, MGN medial geniculate nucleus, MPul medial pulvinar, VA ventral anterior, VL ventrolateral, VPL ventral posterolateral, VPM ventral posteromedial, Rt reticular thalamus.