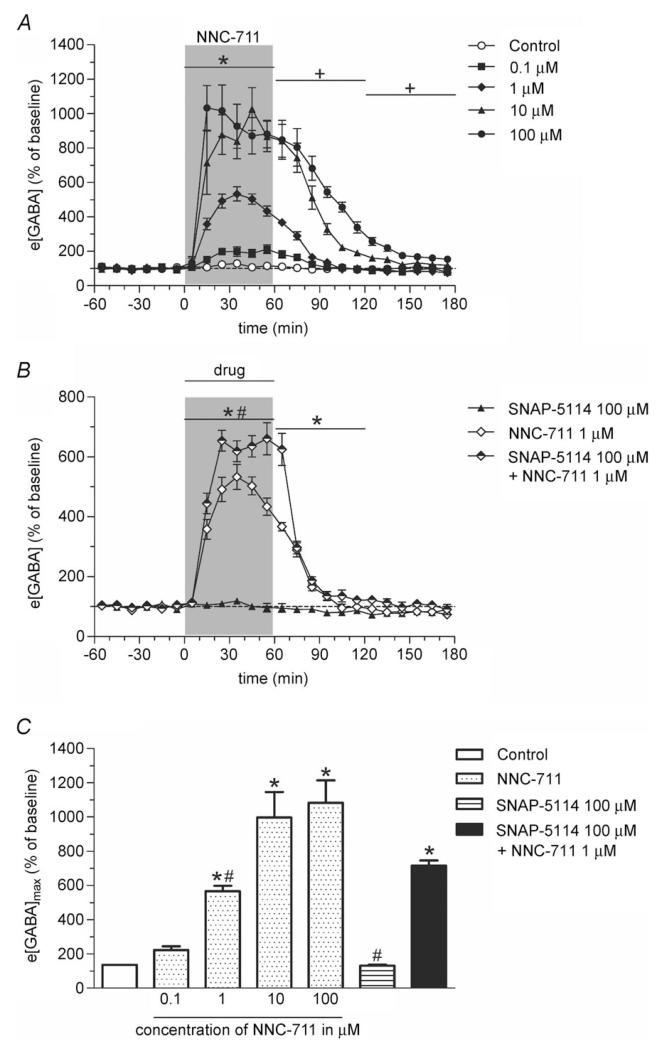
Figure 1. The GAT-1 inhibitor NNC-711 and the GAT-3 inhibitor SNAP-5114 increase e[GABA] synergistically in the rat hippocampus.
A, reverse dialysis of NNC-711 causes a dose-dependent increase in hippocampal e[GABA]. After 1 h of baseline sampling, NNC-711 (0.1, 1, 10 or 100 μm; n = 4–5; filled symbols) or 1% DMSO in Ringer’s solution (control; n = 3; open symbols) was perfused for 60 min through the microdialysis probe (shaded bar) followed by a 2-h washout period with Ringer’s solution. Samples were collected every 10 min. Significance: *1, 10 and 100 μm NNC-711 significantly different from control; +10 and 100 μm NNC-711 significantly different from control (both P < 0.001; Dunnett post hoc test). B, perfusion (shaded bar) of SNAP-5114 (100 μm; n = 5; filled symbols) for 60 min has no effect on hippocampal e[GABA]. Co-perfusion of SNAP-5114 with 1 μm NNC-711 (n = 5; half-filled symbols) caused a significantly larger increase in e[GABA] as compared with infusion of NNC-711 alone (n = 4; open symbols). *NNC-711 and NNC-711 + SNAP-5114 significantly different from SNAP-5114; #NNC-711 + SNAP-5114 significantly different from NNC-711 (both P < 0.001, Bonferroni post hoc test). C, maximal increase in e[GABA] (e[GABA]max; as derived from data in A and B). Co-perfusion of the GAT-1 and GAT-3 inhibitor causes a significantly larger maximum increase in e[GABA] as compared with perfusion of either inhibitor alone. *Significantly different from control (P < 0.05, Dunnett post hoc test); #significantly different from NNC-711 + SNAP-5114 (P < 0.01, Bonferroni post hoc test). All values are expressed as percentage of baseline (mean ± SEM).