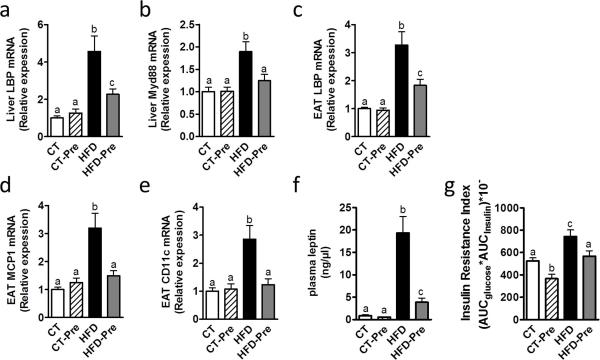
Figure 8. Prebiotic treatment decreased inflammation, fat mass development and insulin resistance associated with HFD diet-induced obesity.
Inflammatory markers mRNA expression: (a) Lipopolysaccharide binding protein (encoded by LBP) and (b) Myeloid differentiation primary response gene (88) (encoded by Myd88) in the liver; (c) Lipopolysaccharide binding protein (encoded by LBP); (d) Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (encoded by MCP1) and (e) Cluster of differentiation 11c (encoded by CD11c) in the epididymal adipose tissue; (f) Plasma leptin (ng/μl) in cava vein and (g) Insulin resistance index determined by multiplying the area under the curve (from 0 min to 15 min) of blood glucose and plasma insulin following an oral glucose load (2g glucose per kg of body weight) measured in control-diet-fed mice (CT) (n = 9), CT-diet-fed mice treated with prebiotics (CT-Pre) (n = 10), HFD-diet-fed mice (HFD) (n = 10) and HFD-diet-fed mice treated with prebiotics (HFD-Pre) (n = 10). Data are means ± s.e.m. Data with different superscript letters are significantly different (P<0.05) according to a post-hoc ANOVA one-way statistical analysis