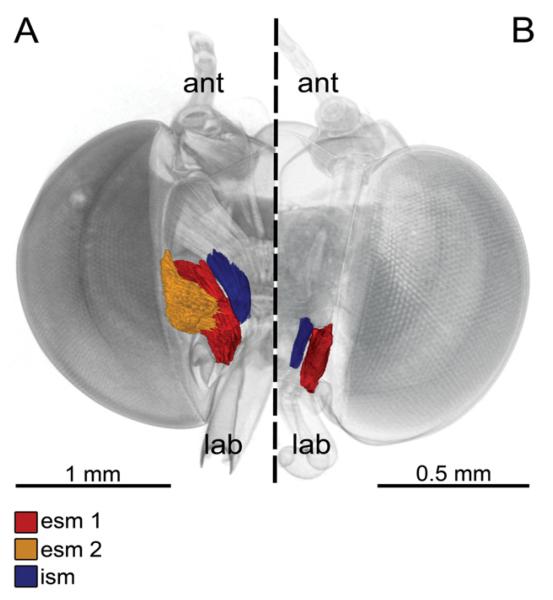
Figure 3. 3D reconstruction based on micro-computed tomography images of the stipes pump of long-tongued (A) and short-tongued (B) Riodindae, frontal view, proboscis removed.
A, Eurybia lycisca (long-tongued): right half of the head with two external and one internal stipes muscles. External stipes muscle 1 (esm 1) originates on the gena and extends to a broad apodeme of the flat stipes part. External stipes muscle 2 (esm 2) originates on the tentorium and extends to the flat part of the stipes. The internal stipes muscle (ism) originates on the tentorium and extends to the stipes near the galeal base (ant, antenna; lab, labial palpus). B, Sarota gyas (short-tongued): left half of the head with one external and one internal stipes muscle. Esm 2 is missing in all short-tongued species.