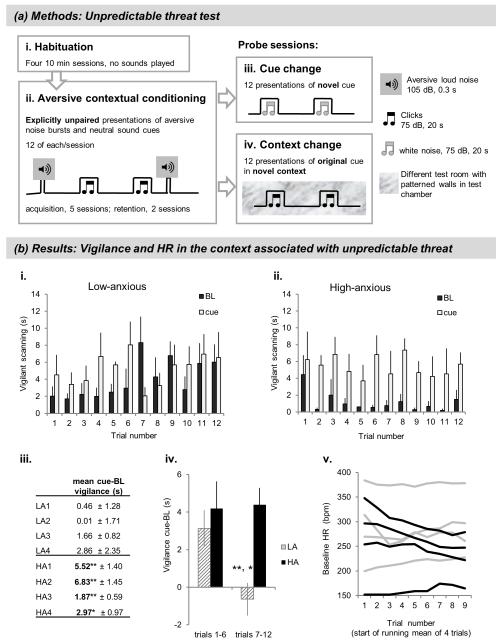
Figure 3. Unpredictable threat test.
(a) Methods. Vigilant scanning behavior (active visual search of the surroundings, accompanied by tense postures marked by forward extension of body and/or head and rearing (Mikheenko et al, 2010; Shiba et al, 2014)) was assessed in the unpredictable threat test, as duration of the behavior over 20 s cue and 20 s baseline (pre-cue) periods. (i) Habituation consisted of four 10-min sessions with no sounds presented. (ii) Acquisition and retention of aversive contextual conditioning comprised daily 30-min sessions. The volume of the aversive noise was sufficient to elicit a bodily startle response, but was somewhat lower than that used in other studies (116-120 dB, Shiba et al 2014, Zeredo et al, 2014) in order to ensure that high-anxious animals would still voluntarily enter the carry box. Inter-stimulus interval = 40-80 s. (iii) Acquisition was followed by the presentation of a neutral, novel cue in the context associated with unpredictable aversive noise (cue change) but in the absence of the aversive noise. Length of session approx. 30 min; inter-stimulus interval = 40-160 s. (iv) Cue change was followed by retention and a context change session, in which the marmoset was placed into a novel, visually distinct context and presented with the neutral, familiar cue that had been played during acquisition/retention, again in the absence of aversive noise. Length of session approx. 30 min; inter-stimulus interval = 40-160 s. (b) Results. (i) Vigilance in the threatening context, low-anxious group. (ii) Vigilance in the threatening context, high-anxious group. (iii) Individual cue-specific vigilance scores (mean across the session),*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. baseline. (iv) Cue-specific vigilance changes in first vs. second half of the session, *p < 0.05 vs. LA trials 1-6; **p < 0.01 vs. HA trials 7-12. (v) Baseline HR in the threatening context. Black lines: high-anxious, gray lines: low-anxious animals.