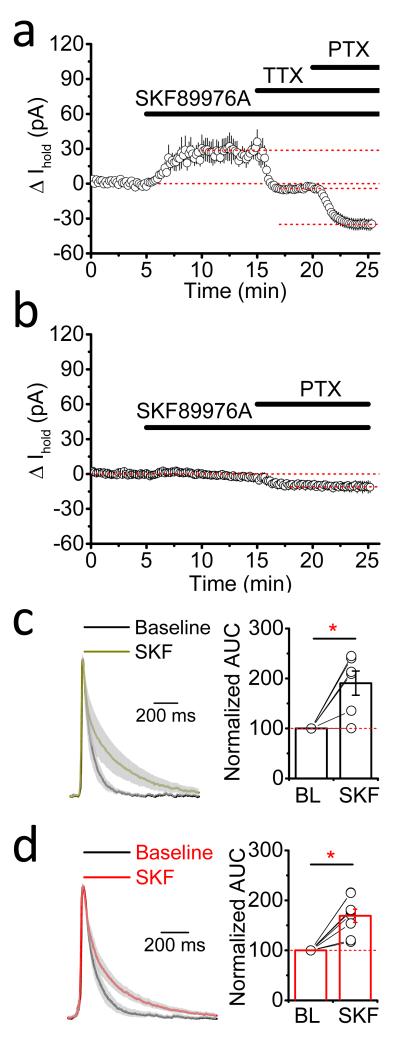
Figure 4. GAT-1 does not revers during epileptiform activity.
(a) Changes in tonic GABAAR-mediated currents in CA1 pyramidal neurons following application of SKF899976A during ongoing epileptiform activity (n = 6; TTX, tetrodotoxin; PTX, picrotoxin; error bars, s.e.m.). (b) The effect of GAT-1 inhibition on tonic GABAAR-mediated currents in CA1 pyramidal neurons in the absence of synaptic GABA release (slices pre-incubated in 1 μM concanamycin; n = 6; error bars, s.e.m.). (c,d) Mean normalized traces of GABAAR transients (gray: s.e.m.) show that SKF89976A similarly prolongs burst-associated GABAAR transients in pyramidal neurons from control (c; area under the curve, AUC, increases from 88.8 ± 18.2 to 188.6 ± 53.9 ms; n = 6; p = 0.038, paired t-test) and epileptic hippocampi (d; AUC increase from 107.9 ± 21.6 to 173.3 ± 24.8 ms; n = 8; p = 0.0012, paired t-test). Bars, mean; error bars, s.e.m.; circles, individual experiments.