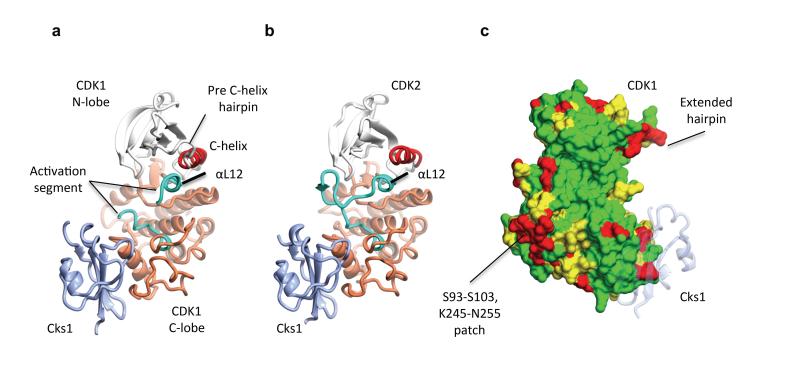
Figure 1. Structure of monomeric CDK1 bound to Cks1 and comparison with CDK2–Cks1.
The complexes are shown in an identical view in panels a and b, and rotated by circa 60 degrees around a vertical axis in panel c. (a) CDK1-Cks1, (b) CDK2-Cks1 (PDB code 1BUH, 31). In both panels the CDK N- and C-terminal lobes are coloured white and coral respectively and the Cks subunit is coloured ice blue. Key regulatory elements are also highlighted: C-helix (CDK1 and CDK2 residues 47-57, red) and activation segment (CDK1 and CDK2 residues 146-173 and 145-172 respectively, cyan). (c) Sequence conservation between human CDK1 and CDK2 mapped onto the surface of CDK1 bound to Cks1. Identical residues (green), conserved residues (yellow) and non-conserved (red) as defined by CCP4MG 70. The structure of Cks1 is shown in semi-transparent ribbon representation to indicate the location of its binding site.