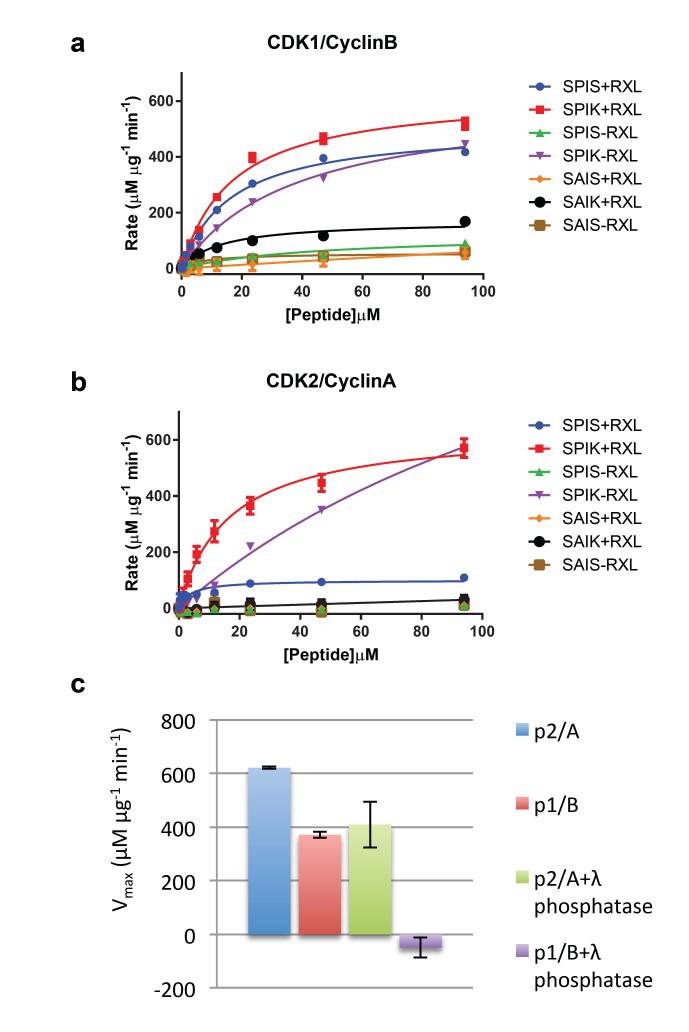
Figure 5. CDK1-cyclin B and CDK2-cyclin A activity.
Seven peptide substrates derived from the sequence of p107 that systematically differ in the residues occupying the P+1 and P+3 sites (where P is the site of phospho-transfer) and whether the KRXL motif that binds to the cyclin recruitment site is present or absent were tested as substrates of CDK1-cyclin B (a) or CDK2-cyclin A (b). Two independent experiments were conducted with duplicate measurements for each point. Error bars on the observed data correspond to the range of observed values. The legend for each line indicates the local sequence around the phosphorylated serine (SPIK, SPIS, SAIS or SAIK), and whether an RXL motif was present (sequence KRRL, denoted ‘+RXL’) or absent (sequence AAAA, denoted ‘−RXL’). (c, d) Table of kcat/Km, peptide values derived from Michaelis Menton fit to the data shown in (a, b) respectively. (e) Activity towards the optimal peptide (SPIK+RXL) was re-determined following incubation of CDK1-cyclin B and CDK2-cyclin A with and without λ-phosphatase. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of two independent measurements.