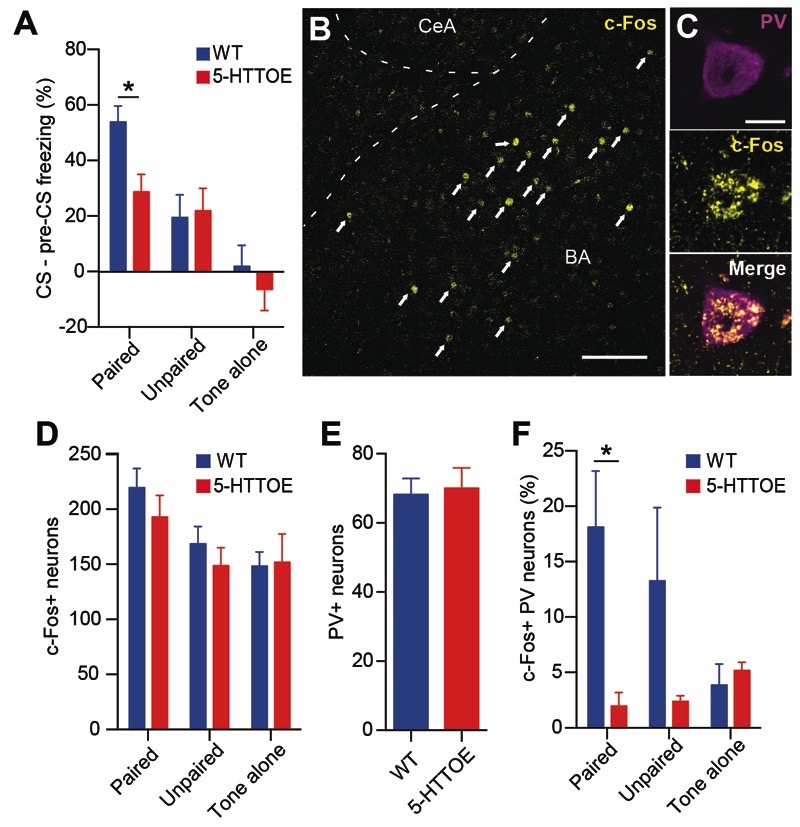
Figure 1. Increased 5-HTT expression leads to reduced fear recruitment of PVINs in the BA.
A) Reduced freezing responses in 5-HTTOE mice in the CS-US paired condition during fear testing session (paired: WT n=14, 5-HTTOE n=12; unpaired: WT n=7, 5-HTTOE n=7; tone alone: WT n=8, 5-HTTOE n=8. B) Representative c-Fos expression in the BA following the fear testing session. Arrows indicate c-Fos+ neurons. Scale bar: 100 μm. C) Immunoreactivity of a representative neuron for PV and c-Fos. Scale bar: 10 μm. D) Overall numbers of c-Fos+ neurons in the BLA do not differ between WT and 5-HTTOE mice following the fear testing session (n=5 per genotype and condition). E) Overall numbers of PV+ neurons in the BA do not differ between WT and 5-HTTOE mice following the fear testing session (n=5 per genotype). F) Reduced numbers of c-Fos+/PV+ in the BA of 5-HTTOE in the paired condition. No significant difference between WT and 5-HTTOE in the unpaired and tone alone condition (n=5 per genotype and condition). * p<0.05.