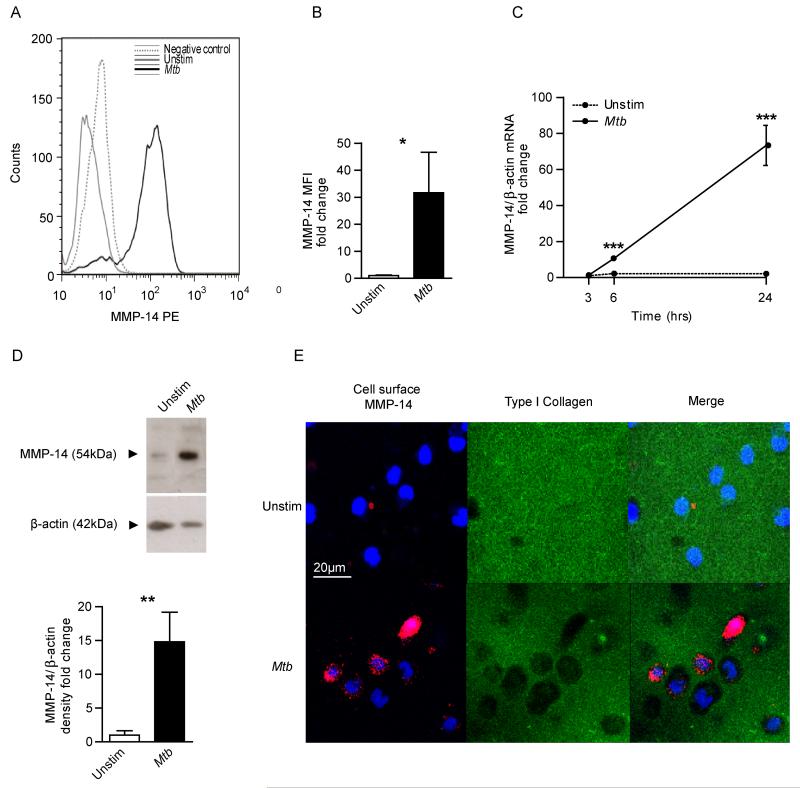
Figure 2. Mtb infection drives monocyte MT1-MMP expression and collagen degradation.
A. Human monocytes were infected with Mtb (Multiplicity of infection = 1) and MT1-MMP expression was analysed by flow cytometry at 24h. Increased MT1-MMP surface expression is demonstrated by greater median fluorescence intensity (MFI). B. MFI analysis confirms increased MT1-MMP expression. C. Mtb infection causes a progressive increase in MT1-MMP mRNA accumulation infected monocytes (normalised to β-actin). D. Mtb infection increases total cellular MT1-MMP at 48h analyzed by western blotting, confirmed by densitometric analysis. β-actin was probed as a loading control. E. Mtb infection causes collagen degradation around monocytes. Human monocytes were seeded on wells coated with fluorescently conjugated Type I collagen and infected with Mtb. MT1-MMP surface expression and collagen degradation were analysed by immunofluorescent staining and microscopy. Blue is DAPI nuclear stain, Magenta is MT1-MMP and green Type I Collagen. Increased collagen degradation occurred at 24h in Mtb-infected wells, and MT1-MMP surface expression co-localises with the areas of collagen degradation. For panels B, C and D, the mean +/− SD values of experiments performed in triplicate are shown and are representative of a minimum of 2 independent experiments. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 by Student’s t-test.