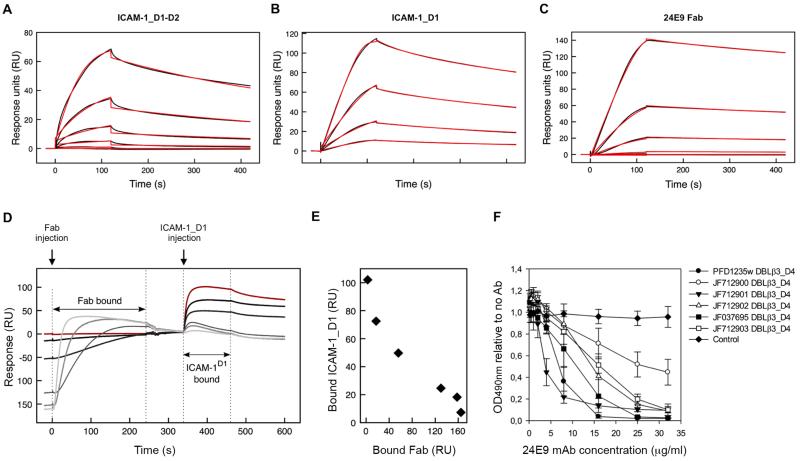
Fig. 3. 24E9 mAb inhibits ICAM-1 binding of DC4 DBLβ3_D4.
PFD1235w DBLβ3_D4 was coupled to a sensor chip surface (Response Units RU=400). Analytes were injected at 45 μl/min with an association phase of 120 s and a dissociation phase of 400 s. Shown are sensorgrams for binding of DBLβ3_D4 to ICAM-1_D1-D2 (A), ICAM-1_D1 (B) and 24E9 Fab (C). Data (black lines) are modeled to a one-site model (red lines). (D) Sensorgrams observed for the sequential binding of 24E9 Fab fragment and ICAM-1_D1 to immobilized PFD1235w DBLβ3_D4. Zero response is taken as the start of injection of ICAM-1_D1. A sensorgram for the binding of ICAM-1_D1 in the absence of 24E9 Fab is shown in red. (E) Quantification of the amount of ICAM-1_D1 binding to PFD1235w DBLβ3_D4 after preincubation of the DBLβ3_D4 with different concentrations of 24E9 Fab. (F) The ability of 24E9 mAb to inhibit DC4 DBLβ3_D4 domains binding to ICAM-1-Fc as assayed by ELISA. Mouse IgG was added as control. Mean OD-values are shown for three independent experiments. Error bars indicate SD.