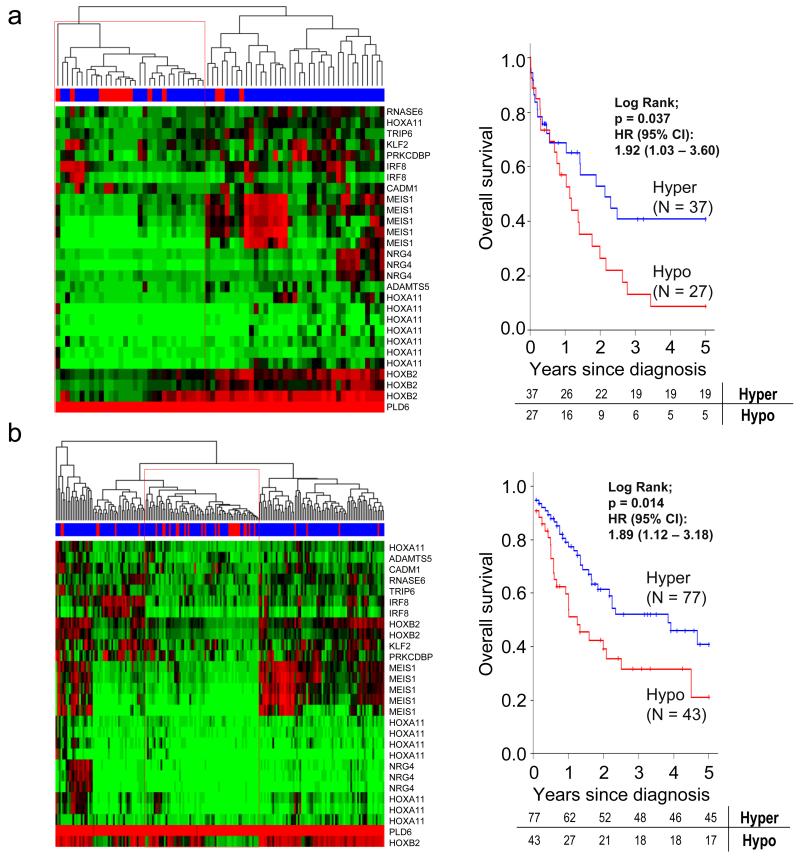
Figure 2.
DNMT3A mutations in AML are associated with a DNA hypomethylation signature characterized by poor patient survival and MEIS1 induction. (a) Hierarchical clustered DNA methylation levels (green: 0%; red: 100%) of 68 AML samples and 28 CpG sites significantly differentially methylated between DNMT3A mutant (red) and wild-type patients (blue). The red boxes indicate samples assigned to the DNMT3A mutant-related hypomethylated cluster. Differential survival analysis (5-year overall survival) of patients within (red line) or outside (blue line) the identified hypomethylated cluster (n=64, right panel). (b) Hierarchical cluster of the 28 CpG sites related to DNMT3A mutation in 194 primary AML patient samples.2 The red boxes indicates samples assigned to the DNMT3A mutant-related hypomethylated cluster. Differential survival analysis (5-year overall survival) of patients within (red line) or outside (blue line) the identified hypomethylated cluster in the independent patient cohort (n=139, right panel).