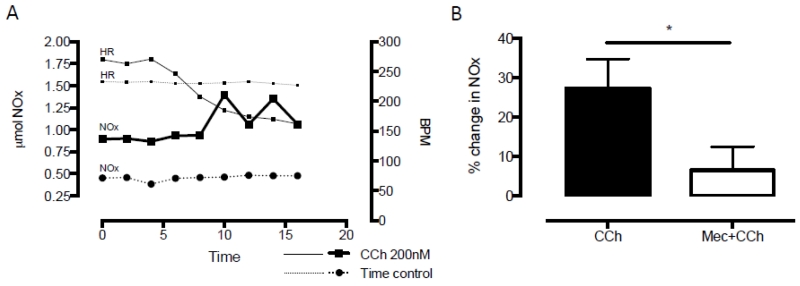
Figure 4. Carbamylcholine perfusion increase the nNOS derived NO metabolite content in coronary perfusate.
A. Experimental data comparing NO metabolite (NOx) levels in coronary perfusate sampled every 2 minutes in time control and during carbamylcholine (CCh, 200nmol/L) perfusion. There is no change in heart rate (HR) or NOx during the time control while CCh results in bradycardia with corresponding increase in NOx levels compared to baseline. B. Summary data demonstrating the increase in NOx levels during CCh perfusion (n=8) and significant reduction if co-perfused with the nicotinic receptor antagonist mecamylamine (Mec, 10μmol/L, *p<0.05, n=8).