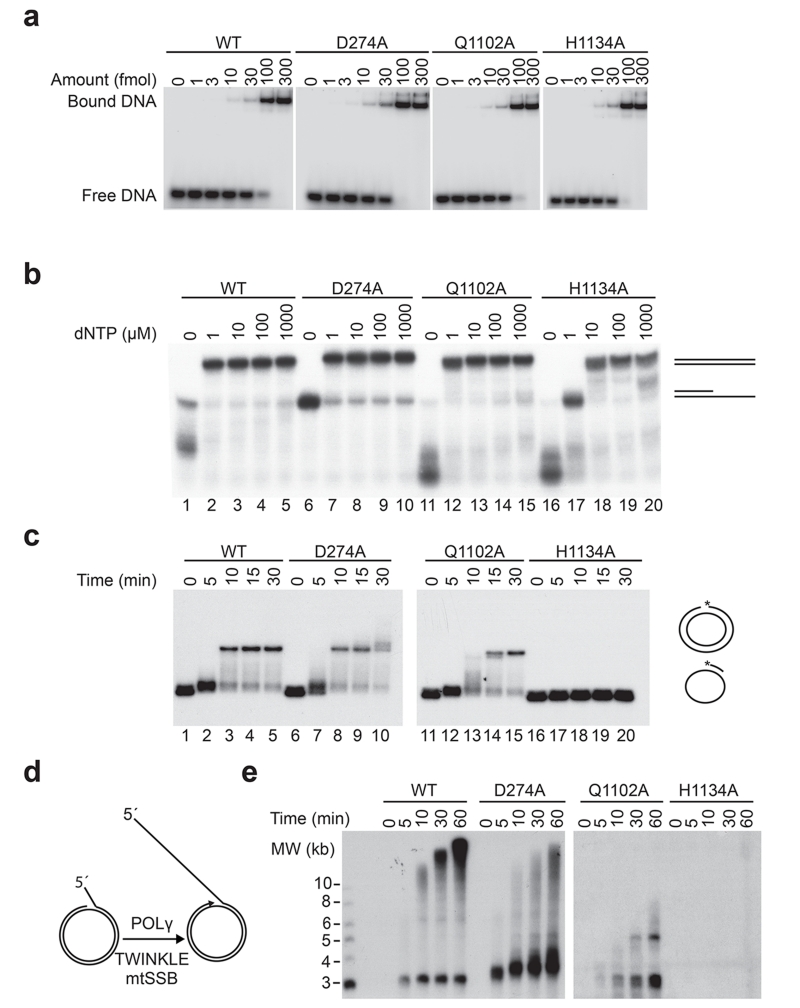
Figure 1. In vitro characterization of HsPOLγA D274A, Q1102A and H1134A mutant proteins.
(a) Representative gels showing electrophoretic mobility assays using WT and mutant HsPOLγ holoenzymes (HsPOLγA/HsPOLγB in complex) to estimate the Kd (DNA) values. Each lane contains 10 fmol of DNA substrate and the indicated amounts of protein complex. Values of dissociation constants presented as an average from three independent binding assays are shown on Table 1.
(b) Coupled exonuclease-polymerase assay. Using the same template as in “a” but in the presence of increasing amounts of dNTPs, H1134A required higher dNTP concentrations than the other HsPOLγA variants in order to polymerize the 35-mer. Reactions were run on a denaturing 15% PAGE.
(c) Second strand synthesis. Q1102A was a slower DNA polymerase than the WT and D274A proteins, whereas H1134A was not able to produced long stretches of DNA. The template consisted of a 5′ radioactively labeled (asterisk represents the labeling) 32-mer hybridized to a single-stranded pBluescript DNA.
(d) Schematic representation of the rolling circle in vitro replication assay used to analyze the function of different HsPOLγA variants in the context of the minimal mitochondrial replisome. In the presence of mtSSB and the TWINKLE helicase, POLγ is able to synthesize long stretches of DNA.
(e) Rolling circle in vitro replication assay. The time curve shows the inability of the H1134A variant to produce long stretches of DNA also in the context of the replisome. Also Q1102A had also problems in generating full-length products. All experiments were repeated at least three times.