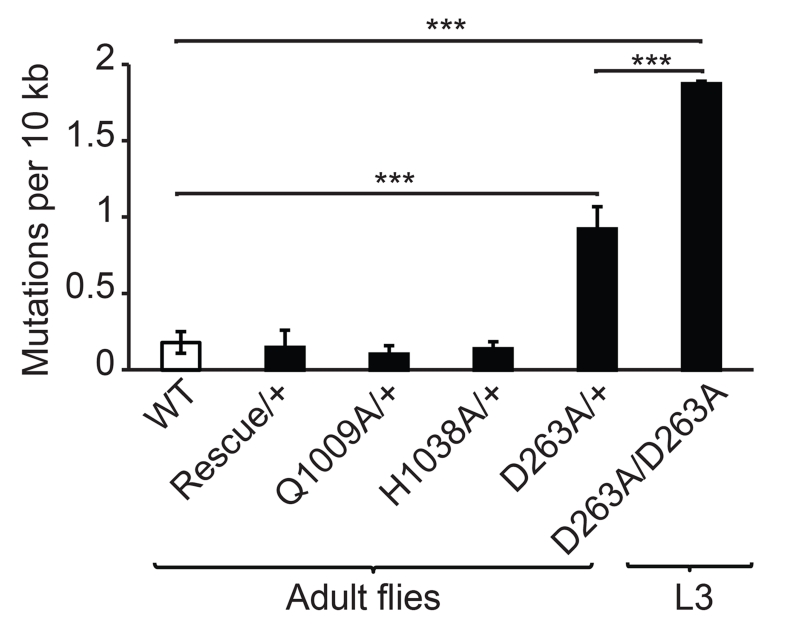
Figure 4. Quantitative assessment of mtDNA mutations in larvae and flies carrying different DmPOLγA alleles.
Post-PCR cloning and sequencing was used to quantify mtDNA mutation load in young adult wild type (WT), genomically engineered heterozygous DmPOLγA flies (Rescue/+, Q1009A/+, H1038A/+, D263A/+) and homozygous exo- larvae (D263A/D263A). If no mutations were detected, the error rate of our method (3.5E-06) was used for further analysis. Bars represent the average number of unique mtDNA mutations. All flies inherited the mutated DmPOLγA allele maternally, hence the detected mtDNA mutations represent both inherited and somatic mutations. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test. ***p<0.001, ** p<0.01, *p<0.05. Error bars represent S.D. n= 3-4.