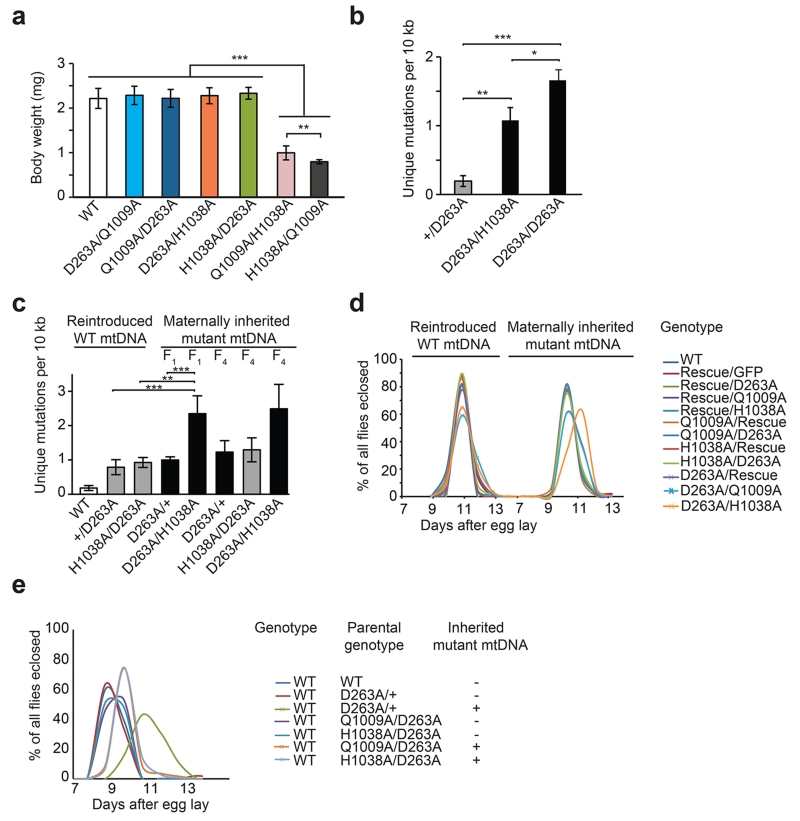
Figure 7. Genetic complementation at the tamas locus.
(a) Comparison of body weight between different DmPOLγA compound-heterozygous larvae. All DmPOLγA compound heterozygous larvae had wild type-like body size. Body weight of twenty 5-day-old larvae was measured and average body weight is shown. Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test. ***p<0.001, ** p<0.01, *p<0.05. Error bars represent S.D. n=20.
(b) Quantification of unique mtDNA mutations in compound heterozygous larvae. The homozygous exo- larvae had significantly more unique mtDNA mutations in comparison with compound heterozygous larvae. Both genotypes inherited mtDNA mutations maternally for one generation. Tukey’s Multiple Comparison test. ***p<0.001, ** p<0.01, *p<0.05. Error bars represent S.D. n=3.
(c) Quantification of unique mtDNA mutations in adult compound heterozygous flies without and with maternally transmitted mutations. Compound heterozygous flies with maternally transmitted D263A exo- allele (black bar) showed increase in the number of unique mtDNA mutations as compared to compound heterozygous flies that inherited the exo- allele paternally (grey bar). One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test. ***p<0.001, ** p<0.01, *p<0.05. Error bars represent S.D. n=3-6.
(d/e) An increase in the mtDNA mutation load affects fly development. Developmental time of different complementation groups is shown. (d) All genomically engineered flies with a clean background (lacking maternally transmitted mtDNA mutations, left panel) had the same developmental time as wild-type (WT) flies. In contrast, all flies inheriting mtDNA mutations maternally for 4 generations (D263A/Rescue, D263A/H1038A and D263A/Q1009A) showed developmental delay (right panel). Crossing schemes are shown on Supplementary Fig. 7a. Data represent two independent experiments. (e) Wild-type (WT) flies carrying mtDNA mutations showed a severe developmental delay. Compound heterozygous flies used in (d) were outcrossed twice in order to replace tamas mutant alleles with wild type tamas allele and clean the nuclear background. All flies had a WT nuclear background with or without maternally inherited mtDNA mutations.