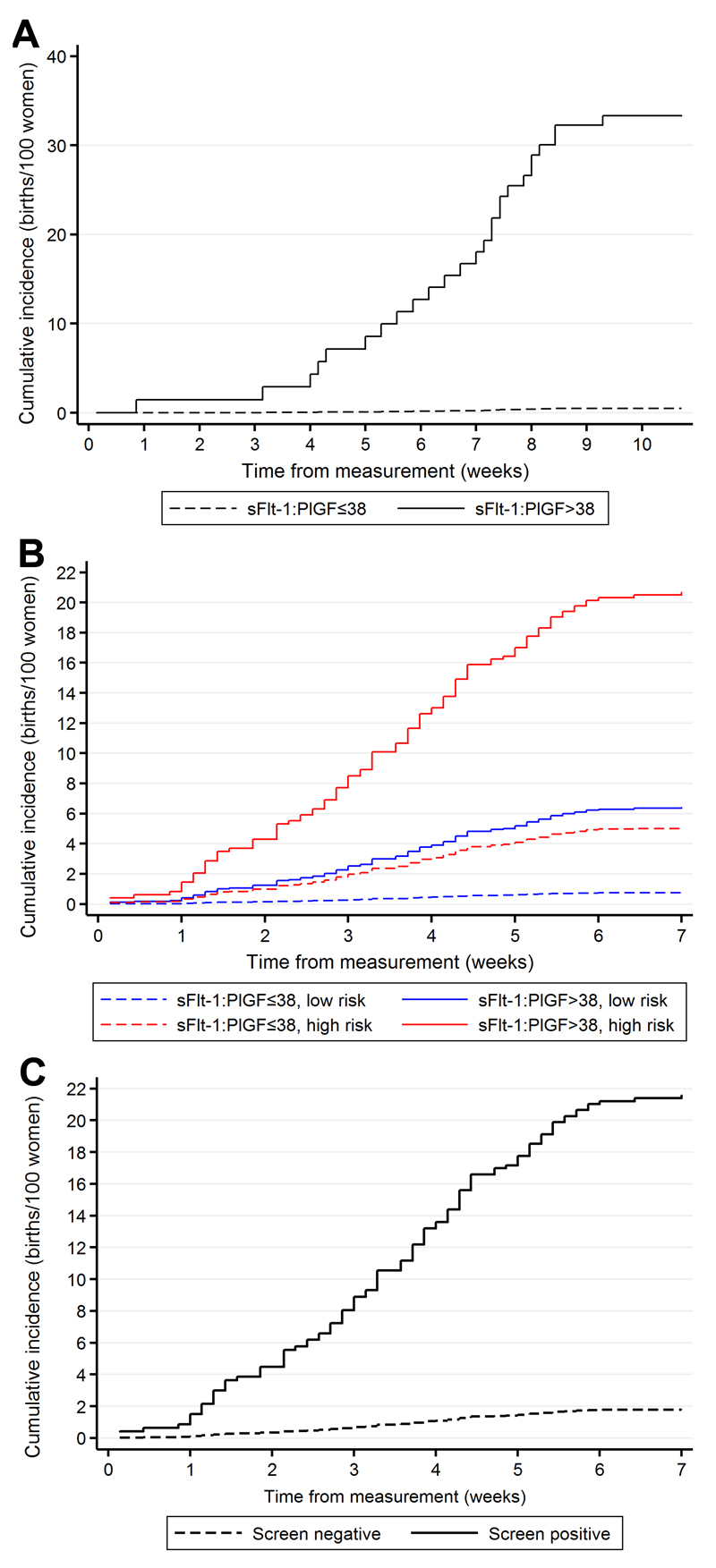
Figure 2.
Cumulative incidence of the primary outcomes (see methods) by the sFlt1:PlGF ratio: A. sFlt-1:PlGF at 28wkGA and preeclampsia leading to preterm birth, B. sFlt-1:PlGF at 36wkGA and severe preeclampsia, stratified by maternal risk. High risk was defined on the basis of maternal risk factors or 20wkGA uterine artery Doppler (see Methods for details), and C. Composite risk status at 36wkGA. Screen positive was defined as (i) sFlt-1:PlGF ratio of >38 AND maternal risk factors OR (ii) sFlt-1:PlGF ratio >110 irrespective of maternal risk factors. Screen negative was defined as all other women. Delivery without the given primary outcome was treated as a competing risk in all three analyses. Hence, the maximum value of the cumulative incidence is the same as the positive predictive value and the curve illustrates the distribution of the timing of the deliveries with the outcome in question.