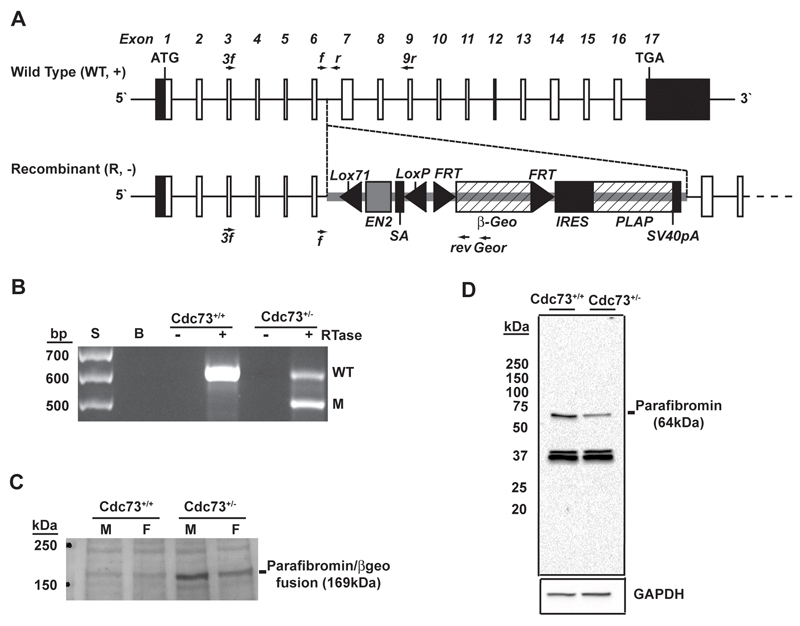
Figure 1. Establishing a conventional Cdc73 knockout mouse model.
(A) Schematic diagram of the Cdc73 gene representing the wild-type (WT, +) and recombinant (R, -) alleles. ATG and TGA represent the start and stop codons respectively. The exons are represented by boxes (open boxes depict translated regions), and the domains within the GeneTrap (Gt) vector, incorporated into the R allele, are labelled. The GeneTrap vector in the RRE190 ES cells from BayGenomics22 referred to as Gt(RRE190Byg) is inserted into intron 6 of the Cdc73 gene and subsumes normal splicing of the Cdc73 exon 6 donor site to the GeneTrap Engrailed2 (EN2) acceptor site with loss of exons 7-17. Thus, the parafibromin-β-geo fusion from the first six exons of the Cdc73 gene, would contain only the N-terminal 170 amino acids, which encompasses the nuclear localisation signal, and lack the remaining 361 amino acids which will encompass the domains that interact with the Paf1 complex, histone methyltransferase complexes16, and β-catenin17, of the wild-type parafibromin. A loss of these critical domains would render the expressed mutant parafibromin non-functional. LoxP (locus of crossing over in phage P1), Lox71 (locus of crossing over 71), FRT (flippase recognition target), SA (splice acceptor of mouse), βGeo (EN2 exon 2, fusion of β-galactosidase and neomycin transferase), IRES (internal ribosome entry site), PLAP (placental alkaline phosphatase) and SV40pA (Simian virus 40 polyadenylation signal). The Lox71, LoxP and FRT sites, located in the GeneTrap vector allow the capability to remove the engrailed intron and β-geo, by breeding with Cre or Flp expressing mice, in order to restore gene function. However, this was not undertaken for this study. (B) Identification of wild-type (Cdc73+/+) and heterozygous (Cdc73+/-) mice by RT-PCR using template RNA extracted from kidneys of adult mice and primers (3f, 9r and rev). The sizes of the wild-type (WT) and mutant (M) bands are 593 bp and 500 bp respectively. RTase, reverse transcriptase; S, size marker; B, blank. (C) Western blot analysis of kidney lysates from adult Cdc73+/+ and Cdc73+/- mice, utilising an anti-β-geo antibody, revealed the expression of a parafibromin/beta-geo fusion protein (169 kDa) in Cdc73+/- knockout mice only. M = male, F = female. (D) Analysis of parafibromin expression (64 kDa) using an anti-parafibromin antibody (A300-171A) revealed a 50% reduction in expression assessed by densitometry of band intensity normalised for GAPDH expression (n=4) in Cdc73+/- mice compared to Cdc73+/+ mice; the whole Western blot is shown. The specificity of the anti-parafibromin antibody was validated in HeLa cells transfected with siRNA against CDC73 (Supplementary Figure 1). These results also show that only one form of parafibromin of size 64kDa and representing the 531 amino acid protein is expressed by Cdc73, despite the reports of of 6 Cdc73 transcripts in the Ensembl database75. These 6 murine Cdc73 transcripts comprise: transcript 1 which is 11586bp and encodes a 531 amino acid protein; transcripts 2, 4, 5 and 6 which are 3134bp, 3056bp, 2727bp and 1047bp, respectively, in length and are processed transcripts or retained introns that do not lead to protein products; and transcript 3 that is 479bp in length and results in a 73 amino acid protein and subject to nonsense mediated decay. Thus, the observation of only one form of parafibromin of 64kDa, is consistent with the translation of transcript 1 in the Ensembl database75, which results in the 531 amino acid parafibromin. The 37kDa bands, which do not correspond to any translated proteins from the other transcripts, are present with similar intensities in Cdc73+/- and Cdc73+/+ mice (p=0.493, n=4), and are likely to represent non-specific bands. Such non-specific bands, which were not altered by the use of CDC73 siRNA (siCDC73), were also detected in HeLa cells (Supplementary Figure 1).