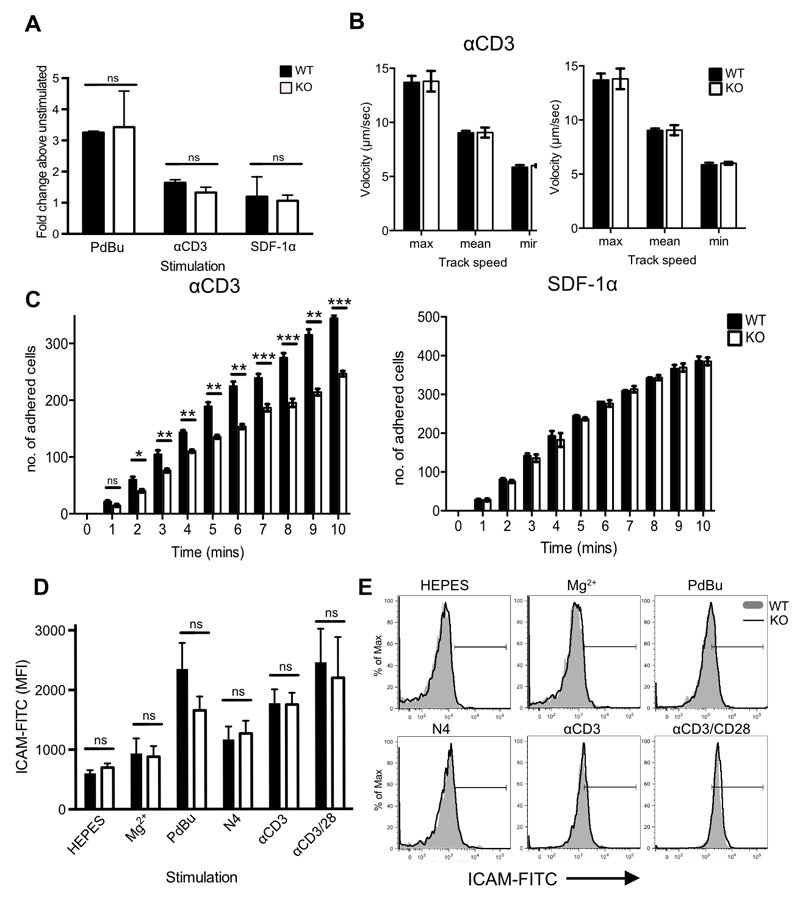
Figure 5. Impaired adhesion to ICAM-1 under conditions of fluid shear stress in the absence of Cav1.
(A) Static adhesion of WT (filled bars) versus Cav1-KO (open bars) CD8 T cells to ICAM-1. CD8 T cells were stimulated with 50nM PdBu, 1μg/mL αCD3 Ab or 5μg/mL SDF-1α before the start of the assay. Fluid shear flow rates were set at 0.3 dynes/cm2. (B) Rolling rates of the cells were analysed in parallel with (C) the number of adherent cells. Data are shown as mean + SEM of data pooled from two independent experiments, each performed in triplicate on two mice per group. NS, not significant; *p ≤0.05, **p ≤0.01, *** p ≤0.001 (Student’s t-test). (D) Cav1-WT or Cav1-KO OT-1 CD8 T cells were incubated for 30 min with chimeric ICAM-1 in HEPES buffer alone or supplemented with 100nM Mg2+, or stimulated with PdBU, N4 peptide, αCD3, or αCD3 + αCD28, as indicated. ICAM-1 bound to T cells was detected by staining with Hu-IgG-FITC. ICAM-1 MFI + SEM from 1 of 3 independent experiments. (E) Representative histograms from each condition, as indicated.