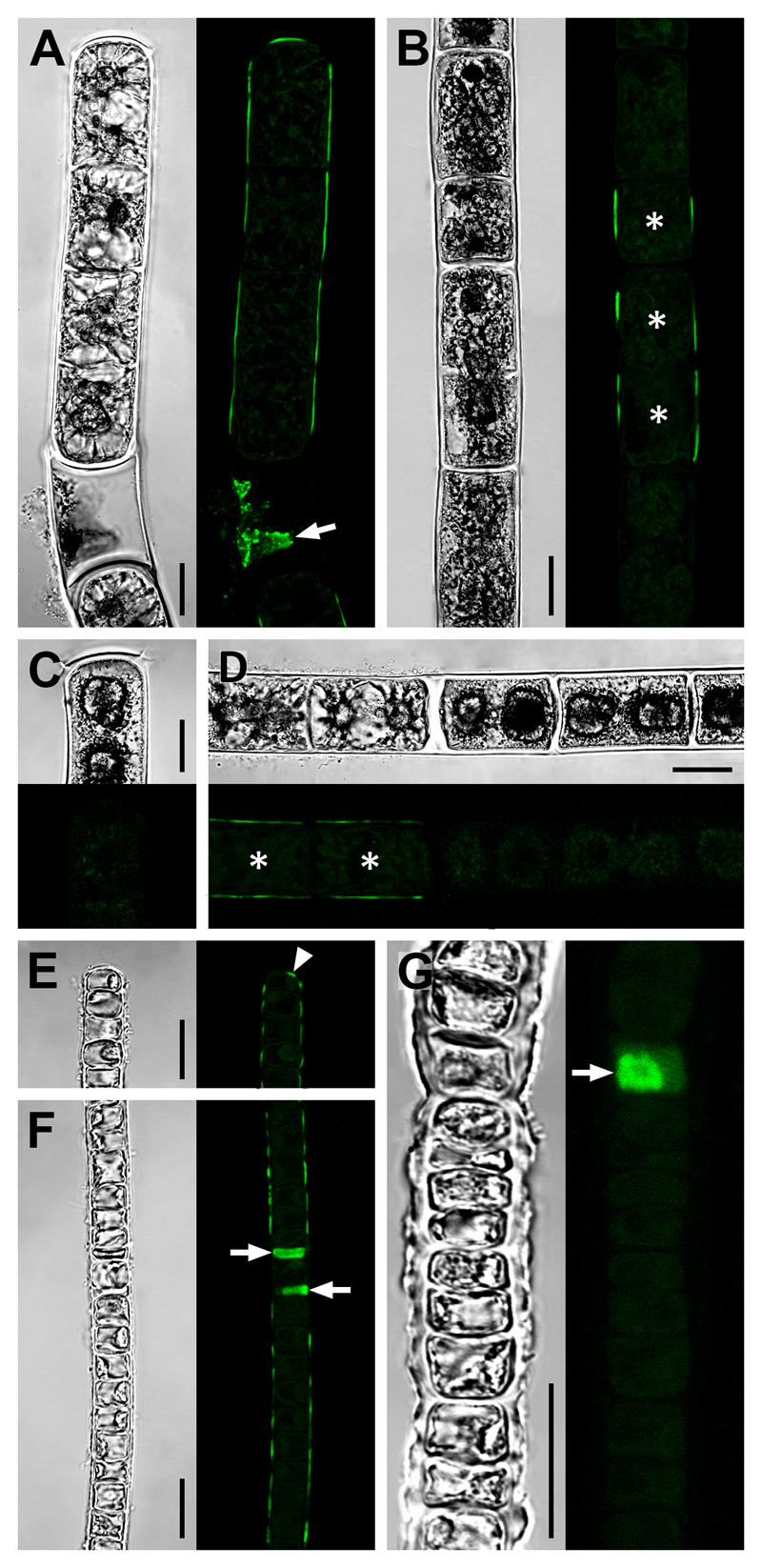
Fig. 3. CLSM micrographs showing integration of the fluorescent acceptor substrate XyGO-SR.
Young (A, E, F) and old (B–D, G) filaments of Zygnema S (A–D) and Klebsormidium crenulatum (E–G) indicative of transglycosylase action. After XyGO-SR incorporation, filaments were incubated in DMF to remove chlorophyll autofluorescence. Cells, which were dead prior to XyGO-SR incubation were seen to contain fluorescent cytoplasmic residue (A, F, G; arrows). Corresponding bright-field images are shown. (A) Filament with fluorescence in outer cell walls and a terminal cross cell wall. (B) Filament showing fluorescence in longitudinal cell walls of short cells (asterisks), but not in longer cells. (C) Terminal cell lacking fluorescence. (D) Filament with fluorescence in outer walls of two vegetative cells (asterisks) but not in adjacent pre-akinetes. (E, F) Filaments with fluorescence in outer cell walls including a terminal cross cell wall (arrowhead). (G) Filament lacking fluorescence in cell walls. Bars = 10 µm.