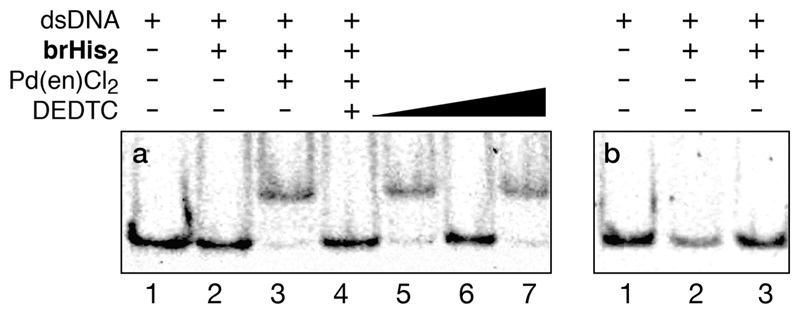
Figure 2.
DNA binding properties of brHis2. (a) Incubation with the target ds-oligonucleotide GTCAT and switching the DNA binding by addition of DEDTC. (b) Incubation with mutated dsDNA MUT. Concentration of the components when present: 75 nM dsDNA, 2 μM brHis2, 20 μM Pd(en)Cl2. (a) Lane 1: dsDNA; lane 2: dsDNA and brHis2; lane 3: previous mixture and Pd(en)Cl2; lane 4: mixture in lane 3 after addition of 50 equiv of DEDTC; lane 5: addition of 60 equiv of Pd(en)Cl2 to the mixture in lane 4; lane 6: mixture in lane 5 after addition of 150 equiv of DEDTC; lane 7: addition of 200 equiv of Pd(en)Cl2 to the mixture in lane 6. All the equiv are expressed relative to brHis2. Samples were resolved on a 10% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel and 0.5× TBE buffer over 40 min at 25 °C and stained with SyBrGold (5 μL in 50 mL of 1× TBE) for 10 min, followed by fluorescence visualization. Oligonucleotide sequences (only one strand shown, brHis2 binding site in bold): GTCAT: 5′-CGC GTCAT AATTGAGAG CGC-3′; MUT: 5′-CGC GTGAT AATTGAGAG CGC-3′.