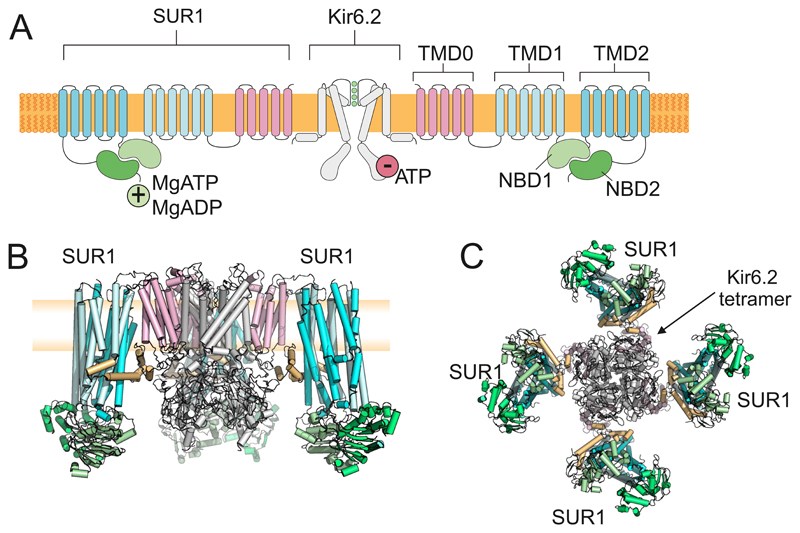
Figure 7.
A: Topology of Kir6.2 and SUR1, showing two (of 4) Kir6.2 and two (of 4) SUR1 subunits. Kir6.2 has two transmembrane domains and cytosolic Na and C termini. SUR1 has 17 transmembrane domains arranged as groups of 5,6 and 6 (TMD0, TMD1 and TMD2) and two nucleotide-binding domains (NBD1 and NBD2) that associate to form 2 nucleotide-binding sites at their interface. Binding of ATP (or ADP) to Kir6.2 inhibits channel activity. Binding of MgADP/MgATP to SUR1 stimulates activity. B-C: The KATP channel complex viewed from the side (B) and bottom (C). The Kir6.2 tetramer is surrounded by 4 SUR1 subunits. In B, the front subunit has been removed for clarity. Blue: TMD1, TMD2 of SUR1. Pink: TMD0 of SUR1. Green: NBDs of SUR1. Grey: Kir6.2. Brown: 3rd cytosolic loop of SUR1. The plasma membrane (yellow) is shown behind the channel in B. Figure provided by Dr M Puljung, Oxford.