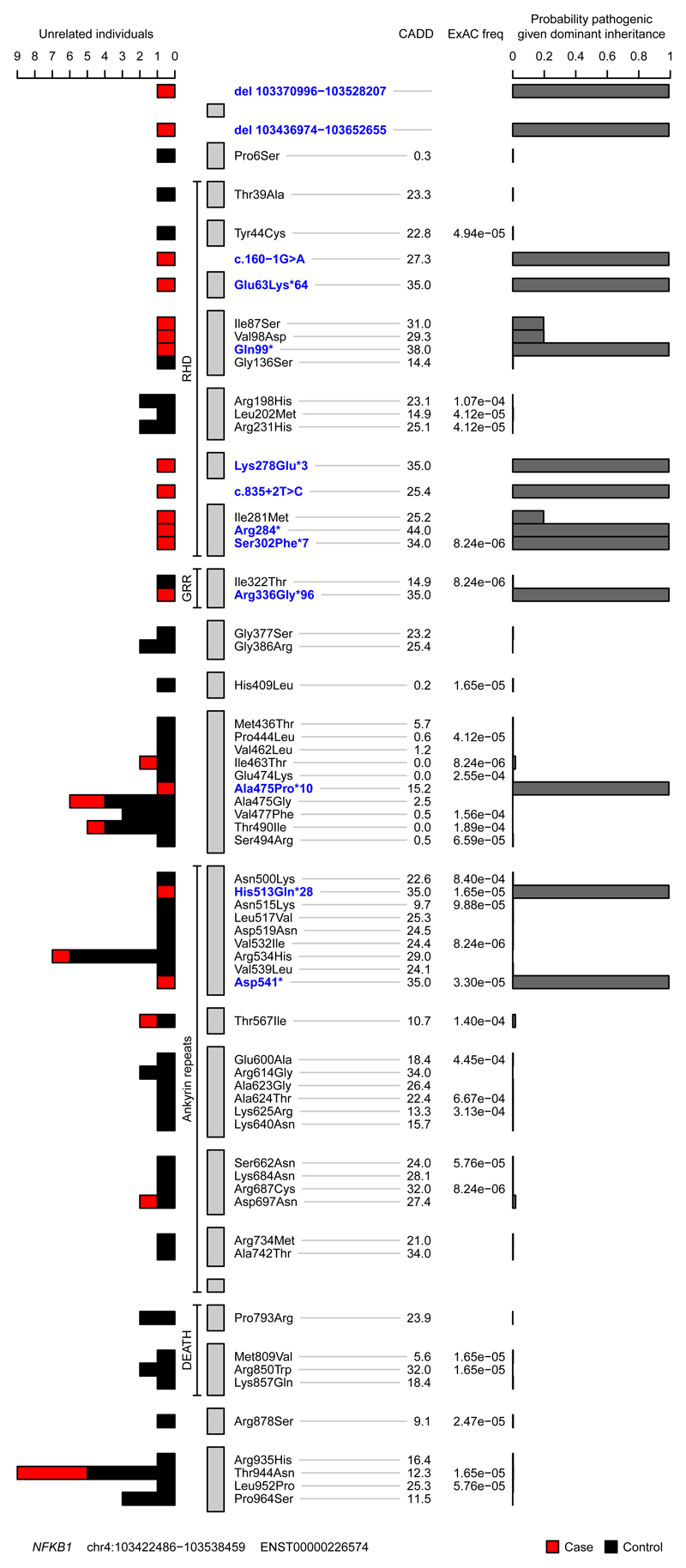
Figure 2. Plot of rare missense, truncating and gene deletion NFKB1 variants identified in the NIHRBR-RD genomes of unrelated individuals, and their location relative to NFKB1 domains.
The tracks from left to right show: number of unrelated case (red) and control (black) individuals in whom each variant was observed; the four major NFKB1 domains; gray bars representing each exon in transcript ENST00000226574; variant annotation relative to transcript ENST00000226574 and genomic location of large deletions, with VEP HIGH impact variants and large deletions highlighted in blue; CADD scores of all nonsense, frameshift, splice and missense variants; ExAC allele frequencies; conditional probability of variant pathogenicity inferred using BeviMed. Only variants labelled as MODERATE or HIGH impact relative to the canonical transcript ENST00000226574 are shown. The initial inference that formed part of the genome-wide analysis included variant chr4:103423325G>A, which was observed in one control sample. This variant is intronic (LOW impact) relative to ENST00000226574 but is a splice variant (HIGH impact) relative to the minor transcript ENST00000505458. As variants were filtered based on the highest impact variant annotation against any Ensembl transcript, this variant was originally included in the inference. For this plot, the inference was re-run including only missense, truncating and gene deletion variants relative to the canonical transcript.