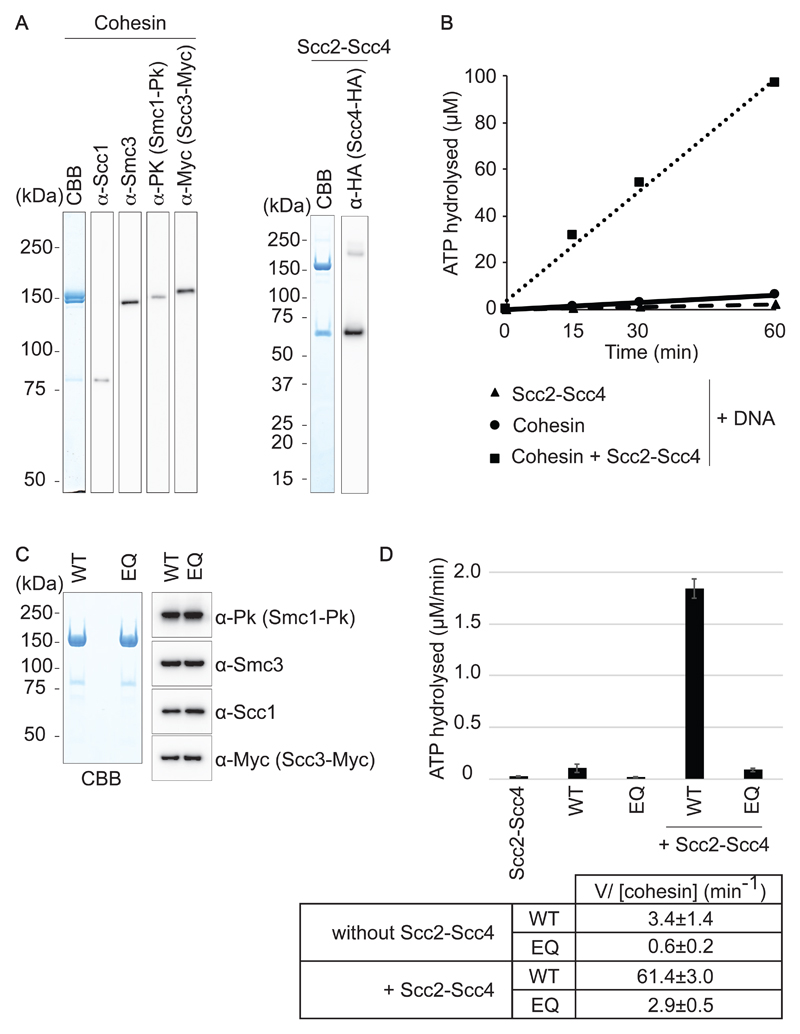
Figure 1. Purification of budding yeast cohesin and its loader.
(A) Purified budding yeast cohesin and cohesin loader were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie Blue staining (CBB) and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (B) Timecourse analysis of ATP hydrolysis by cohesin in the presence of DNA, with or without the cohesin loader. (C) Purified cohesin and Walker B motif mutant EQ-cohesin were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie Blue staining and immunoblotting. (D) Comparison of the ATP-hydrolysis rates of wild-type and EQ-cohesin, in the presence or absence of the cohesin loader. A reaction with the cohesin loader (Scc2-Scc4) but without cohesin served as a negative control. The means and standard deviations from three independent experiments are shown. Hydrolysis rates calculated per cohesin complex are listed.