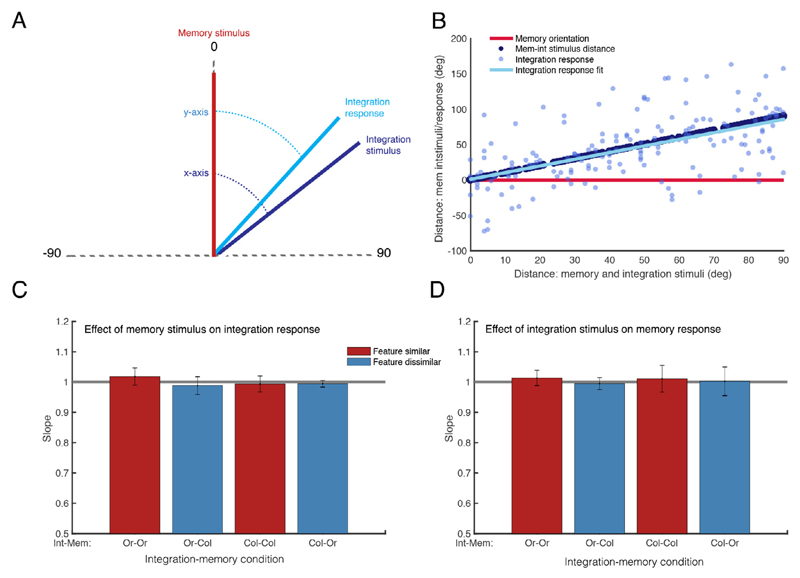
Fig. 5.
Interference between memory and integration stimuli. A: Diagram representing the rotation of shown stimuli and responses such the memory stimulus is zero, and the integration stimuli and responses are always a positive distance from 0. B: Example plot from one participant for orientation integration with orientation memory. The distance between the memory stimulus and integration stimuli/responses (y axis) are plotted against the distance between the shown stimuli (memory and integration stimuli) on the x axis. C: Mean slopes of the fitted regression for the difference between memory stimulus and integration responses. The horizontal black line represents the slope of the difference between memory and integration stimuli. D: Mean slopes of the fitted regression for the difference between integration stimulus and memory responses. All error bars are 95% confidence intervals.