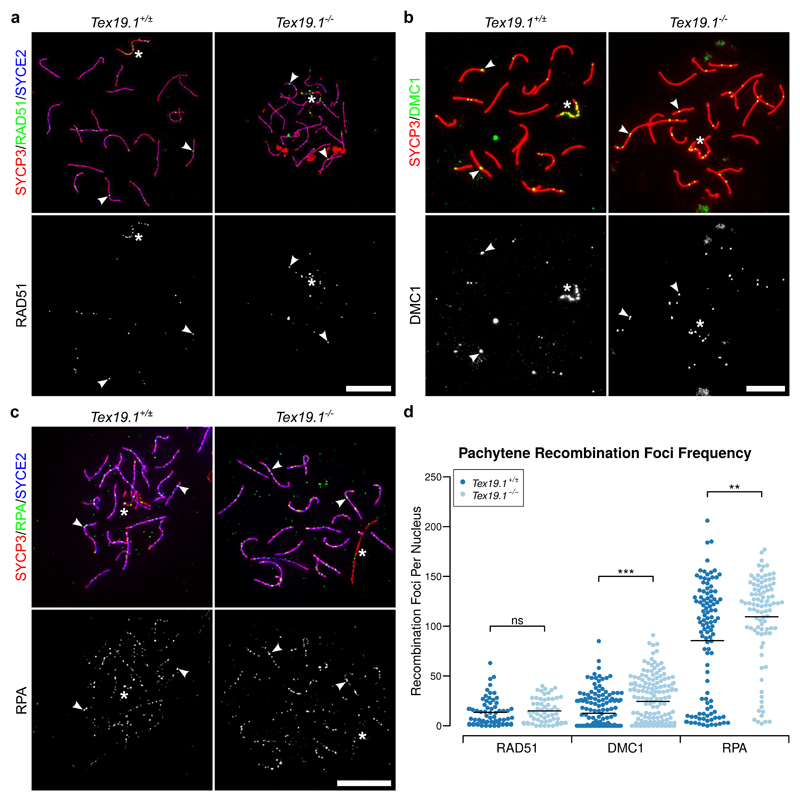
Fig. 1. Autosomally Synapsed Pachytene Tex19.1-/- Spermatocytes Have Increased Numbers of Early Meiotic Recombination Foci.
a-c Immunostaining for RAD51 (a), DMC1 (b) and RPA (c) recombination proteins in Tex19.1+/± and Tex19.1-/- autosomally synapsed pachytene spermatocyte chromosome spreads. The recombination proteins are shown in green, SYCP3 (a-c red) and SYCE2 (a, c blue) mark the lateral and central elements of the synaptonemal complex respectively. Single channel greyscale images for the recombination foci are also shown, foci co-localising with axes were scored as recombination foci. Asterisks indicate sex chromosomes, arrowheads indicate example recombination foci. Scale bars 10 μm. d Scatterplots showing the number of axial recombination foci in autosomally synapsed pachytene nuclei. Means are indicated by horizontal lines. Mean foci frequencies are 13 ± 14, 15 ± 13, 13 ± 17, 24 ± 24, 86 ± 57, 110 ± 44 from left to right across the plot. Number of nuclei analysed were 66, 60, 165, 163, 109, 64 from a total of at least 3 experimental or 3 control animals for each recombination protein. Foci counts were compared between genotypes using a Mann-Whitney U test, asterisks denote significance (** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001), ns indicates no significant difference (p > 0.05).