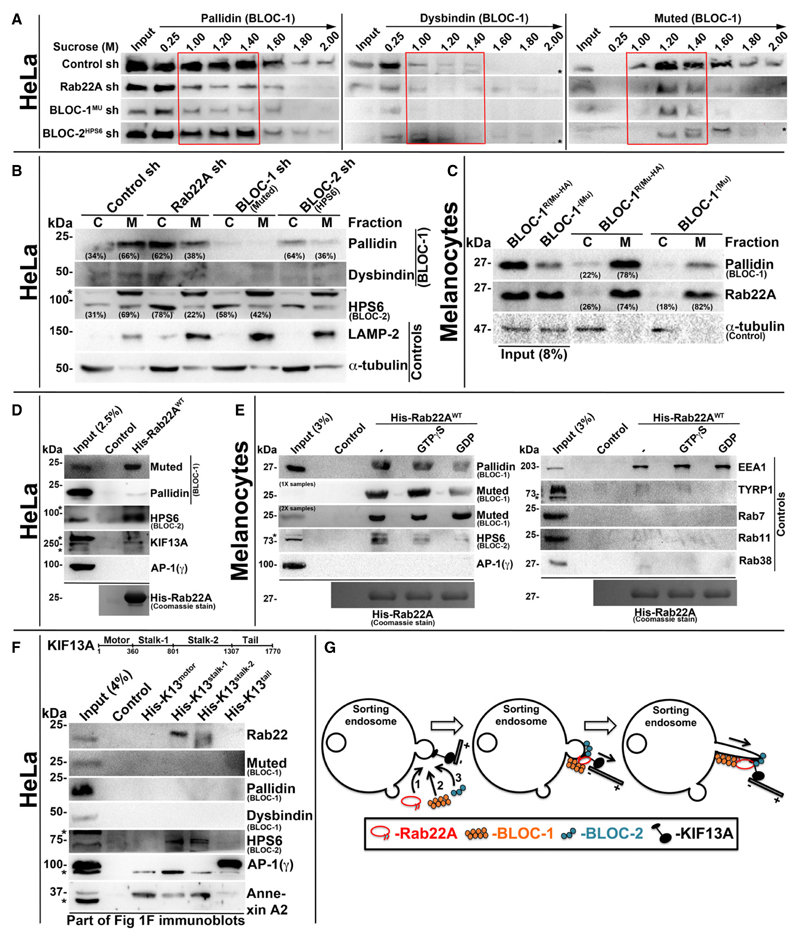
Figure 5. Rab22A regulates membrane association of BLOC-1 and BLOC-2, and forms a complex with BLOC-1-BLOC-2-KIF13A.
A Subcellular membrane fractionation of control and Rab22A-, BLOC-1-, BLOC-2-knockdown HeLa cells and probed the fractions for pallidin, dysbindin and muted. Red coloured box emphasizes BLOC-1 membrane association in the respective cell types.
B, C Membrane-cytosol fractionation of homogenates from HeLa cells (B) or melanocytes (C) as indicated. Protein band intensities were quantified and indicated the percentage membrane association on the gels.
D, E Pull-down of His-Rab22AWT using HeLa (D) or melanocyte (E) lysate. In (E), the beads were preloaded with GTPγS or GDP.
F Pull-down of different His-KIF13A domains using HeLa cell lysate.
G Model illustrating the recruitment (left) and association (middle) of Rab22A, BLOC-1 and BLOC-2 in a sequential manner onto the membrane buds of E/SEs followed by interaction with KIF13A motor. Rab22A-BLOC-1-BLOC-2 complex possibly extends the membrane buds into RE tubules with KIF13A motor (right) movement on microtubules.
Data information: In (A–F), * indicates non-specific bands. In (D–F), the bead-bound His-Rab22A/His-KIF13A domains were shown on the Coomassie-stained gels separately or in Fig 1F.