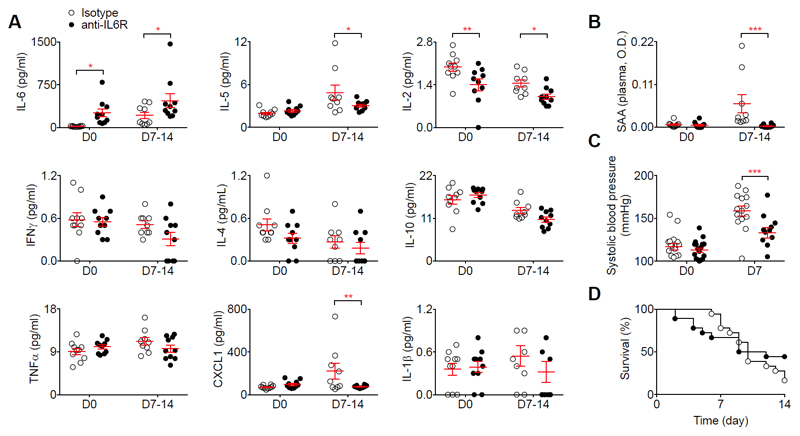
Figure 2.
Anti-IL6-R prevents angiotensin II induced hypertension but does not protect against aortic rupture induced by angiotensin II and anti-TGFβ infusion. Mice were treated with anti-IL6-R or isotype control (n=22 mice/group) starting one week before angiotensin II and anti-TGFβ infusion. A – Plasma concentration of cytokines at day 0 (before angiotensin II and anti-TGFβ infusion) and day 7 to 14. *p<0.05 isotype vs anti-IL6-R; **p<0.01 isotype vs anti-IL-6R; 2-way ANOVA followed by uncorrected fisher’s test. B – Plasma concentration of serum amyloid A (SAA) at day 0 (before angiotensin II and anti-TGFβ infusion) and day 7 to 14. ***p<0.05 isotype vs anti-IL6-R; 2-way ANOVA followed by uncorrected fisher’s test. C - Systolic blood pressure measurement using tail cuff at day 0 and day 7 after angiotensin II and anti-TGFβ infusion. ***p<0.001 isotype vs anti-IL-6R; 2-way ANOVA followed by uncorrected fisher’s test. D - Survival curves of mice after angiotensin II and anti-TGFβ infusion. All data for the generation of the graphs shown in Figure 2 were generated in two independent experiments and then pooled together.