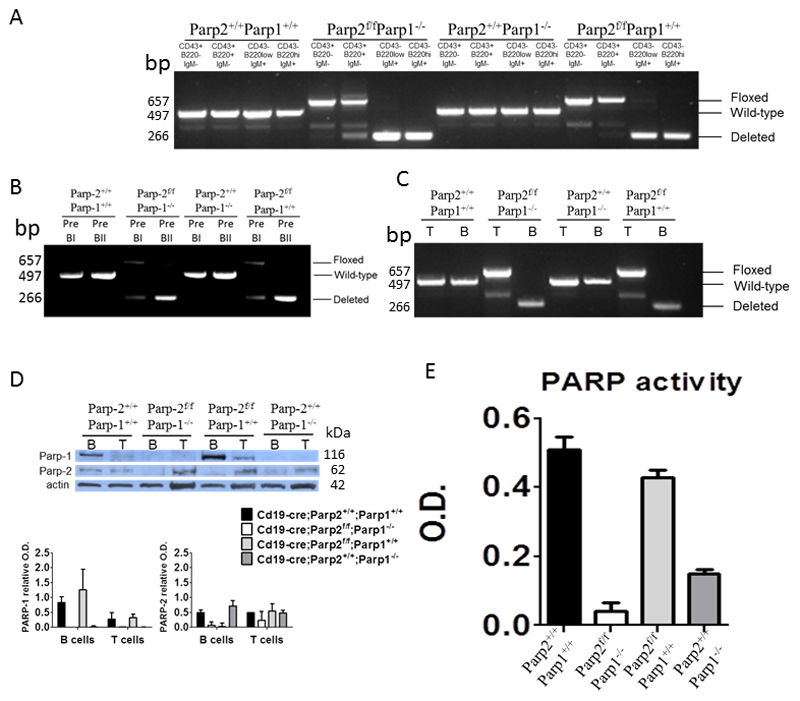
Figure 1. Effectiveness of PARP-2 deletion in Cd19-cre;Parp-2f/f mice.
(A-C) PCR analysis from genomic DNA in sorted bone-marrow (A,B) and splenic (C) B-cell subsets from mice of the indicated genotypes. Pre-BI cells (B220+CD19+IgM-CD25-CD117+); Pre-BII cells (B220+CD19+IgM-CD25+CD117-); T-cells (CD3+); B-cells (B220+) (D) Western-blot analysis of PARP-1 and PARP-2 proteins expression in splenic B and T cells from mice of the indicated genotypes. Expression of β-actin was used as a loading control. Densitometry analysis (optical density) of PARP-1 and PARP-2 bands from western blotting is shown. The results are expressed as mean ± SEM using samples from two different mice of each genotypes. (E) PARP activity in protein extracts from B-cells upon activation with LPS. Resting B-cells were isolated from spleen, cultured in the presence of LPS (10 µg/ml) for 2.5 days, lysed and PARP activity determined in protein extracts. Results represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments carried out in triplicate.