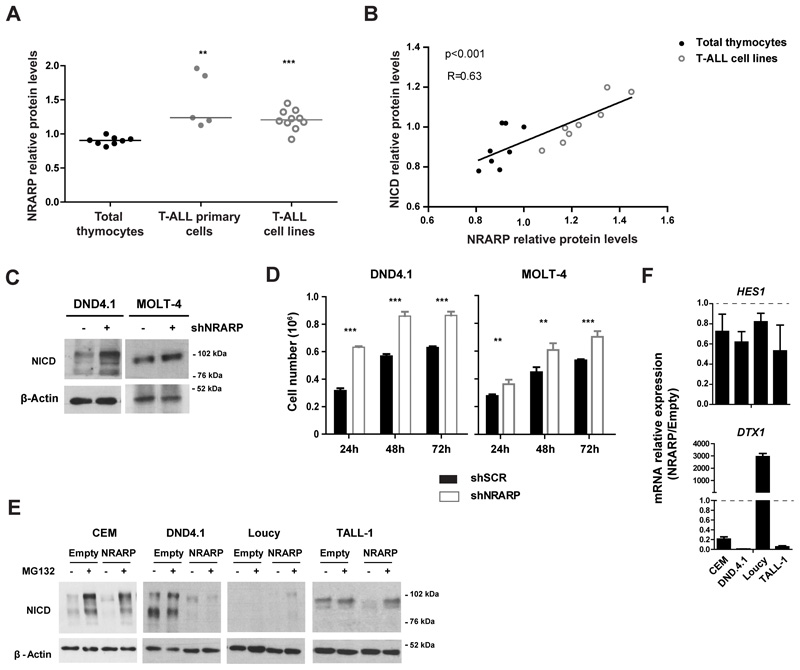
Figure 1. NRARP expression is increased in T-ALL cells but it is insufficient to block Notch signaling.
(A) NRARP protein levels in T-ALL primary cells (n=5) and cell lines (n=10) determined by Western Blot (WB) and normalized to NRARP levels in total thymocytes (n=8). (B) Correlation between NRARP and NICD protein levels in total thymocytes and T-ALL primary cell lines. Protein levels were determined by WB. (C) WB analysis of NICD expression in DND4.1 and MOLT-4 T-ALL cell lines upon NRARP knockdown using shRNAs. (D) Effects of NRARP knockdown in DND4.1 and MOLT-4 cell proliferation. Cells were transduced with a shRNA against NRARP (shNRARP) or a scramble sequence as control (shSCR). Representative assay of 3 biological experiments, each performed in triplicate (E) Effects of NRARP overexpression in T-ALL cell lines NICD levels (determined by WB). To better visualize the changes induced by NRARP overexpression, T-ALL cells transduced with an Empty vector (control condition) or a NRARP vector were treated with the proteasome inhibitor MG132. (F) Relative expression of Notch transcriptional targets in T-ALL cells overexpressing NRARP. mRNA levels were normalized to control condition (Empty cells). In (D) and (F) data represent the mean ± SEM. Statistical values were obtained using either the Student’s t test (A), 2way ANOVA (D) or Pearson correlation (B). **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.