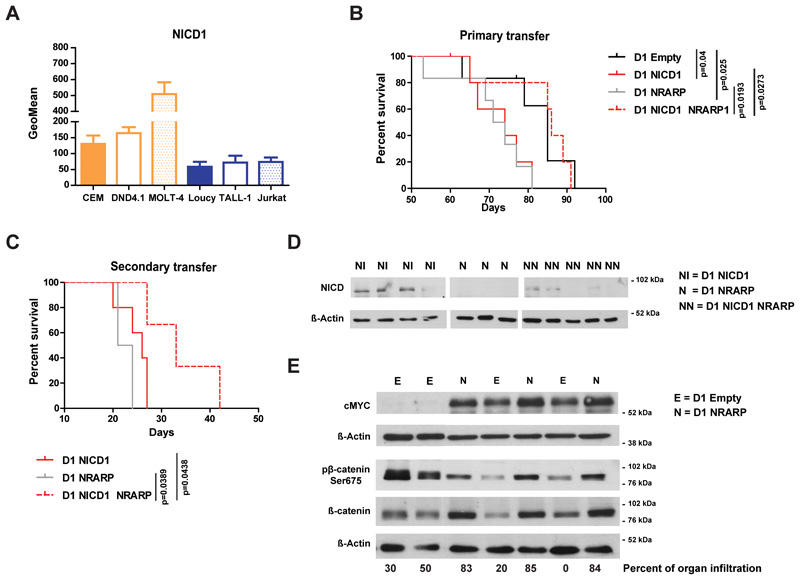
Figure 4. NRARP anti- or pro-tumoral role in T-ALL depends on NICD1 levels.
(A) Flow cytometry analysis of NICD1 levels in T-ALL cell lines (n=3). (B) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of immunocompromised (NSG) mice transplanted with p53-null CD4-CD8- precursor T-cells (D1 cells) overexpressing NICD1, NRARP or both. Whereas NRARP alone induced leukemia development with a similar kinetic of that of NICD1 (median survival of 72.5 and 74 days, respectively), its co-expression with NICD1 had a suppressive effect, increasing significantly the median survival to 86 days (p<0.05). (C) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of NSG mice transplanted with D1 cells isolated from mice primarily transplanted with D1 cells overexpressing NICD1, NRARP or both. The secondary transfer of these cells confirmed their leukemogenic potential and NRARP suppressive role when co-expressed with NICD1 (p<0.05). (D) NICD protein levels in D1 cells isolated from spleens of mice transplanted with D1 NICD1, D1 NRARP or D1 NICD1 NRARP overexpressing cells. (E) Western blot analysis of cMYC, β-catenin and pβ-catenin Ser675 protein levels in cells collected from spleens of mice transplanted D1 NRARP cells and D1 Empty cells (control condition).