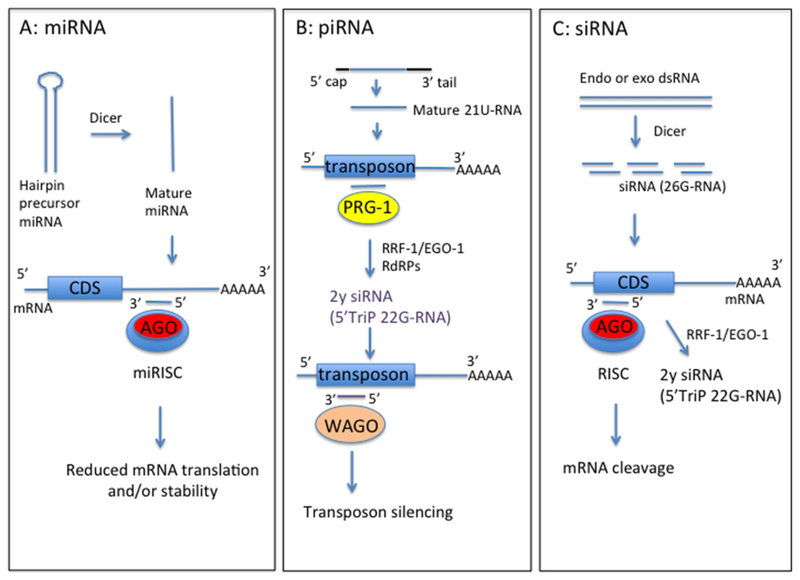
Figure 1.
Schematic of forms and functions of small RNA classes in nematodes, based on C. elegans information. A) Mature microRNA (miRNA) strand, derived from precursor miRNA, is incorporated into the miRNA-induced silencing complex (miRISC) containing Argonaute protein (Ago). This complex directs binding to mRNA target sequences, commonly in the 3’UTR. Binding specificity is determined by complementarity between the target sequence and miRNA seed sequence (nucleotides 2–7). B) Mature Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNA) (21U-RNA) are processed from a capped precursor and bind to Piwi Argonaute PRG-1 to recognize target sequences, often transposons, by imperfect complementary base-pairing. This initiates synthesis of secondary small inhibitory RNAs (siRNAs) with 5’ triphosphate (5’TriP 22G-RNAs) by RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRPs) RRF-1 or EGO-1. 22G-RNAs associate with worm-specific Argonaute proteins (WAGOs) to mediate target silencing. C) Endogenous or exogenous double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) is processed by dicer into siRNAs, which bind anti-sense to mRNA exonic sequence to mediate mRNA cleavage by RDE-1 Argonaute. siRNAs also act as primers for synthesis of 22G-RNAs by RRF-1 or EGO-1 to amplify the RNA interference (RNAi) response, using target dsRNA as a template.